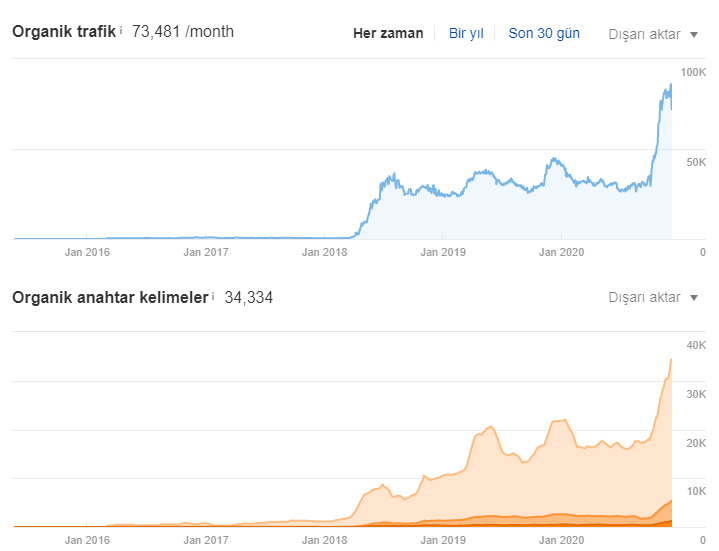
In this SEO Case Study, using Contextual and Conceptual Hierarchies along with Topical Graphs to satisfy every macro and micro Search Intent within a Semantic Search Network will be shown through mainly a real-world SEO Case Study. This SEO Case Study includes four different SEO Success Stories and Projects. The main SEO Project has the result of 0 to 128.000 Organic Traffic in 123 days and 12.000 Organic Clicks per day in 162 days.
This article includes highly and advanced SEO Terminology, Theories, and Concepts. Also, it includes an Executive Summary. You will see the background of the four SEO Projects and the same methodology’s consistent SEO results below.
If you want, you can read a briefer executive summary with only actionable points that have been published on OnCrawl and focuses on the Second Site’s SEO Project mainly.
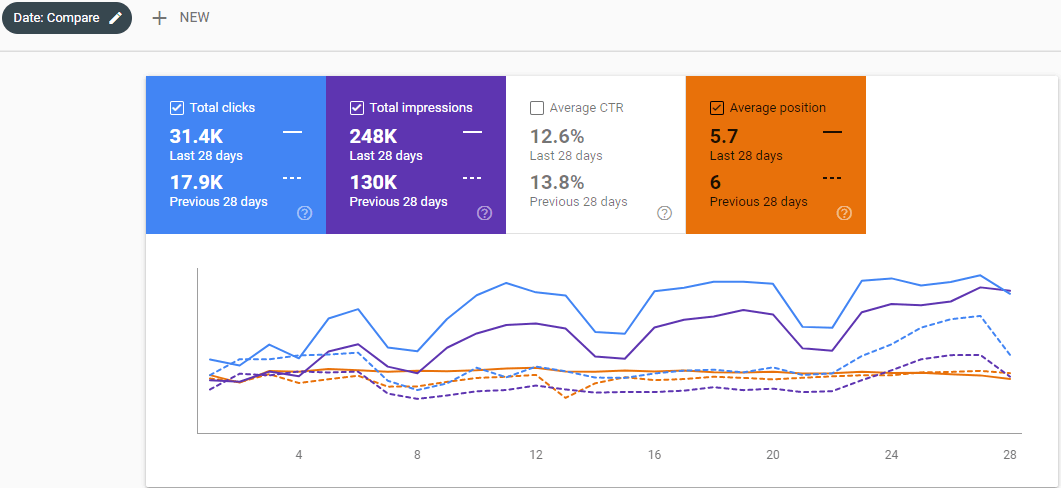
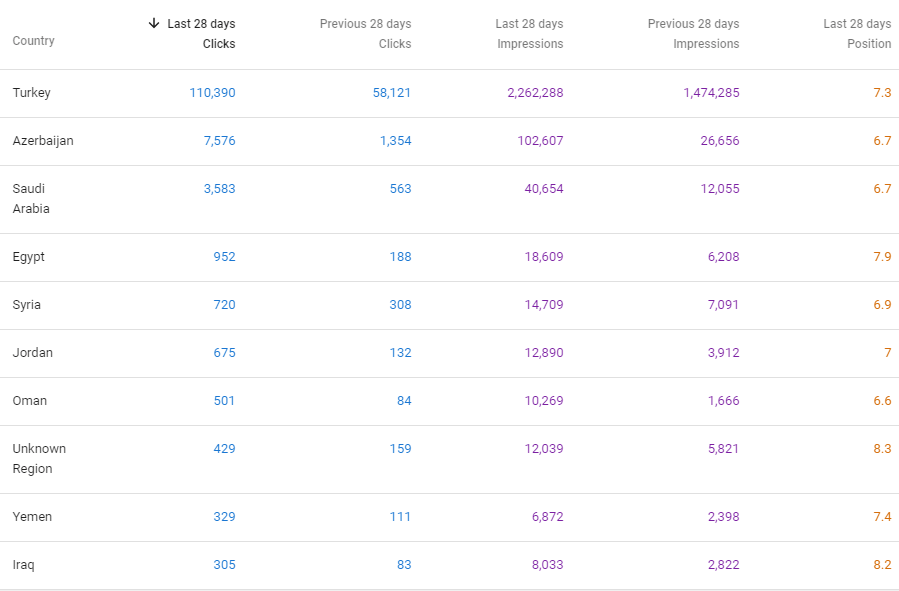
Below, you will see the last 28 Days Comparison from 27th of November, Google Search Console.
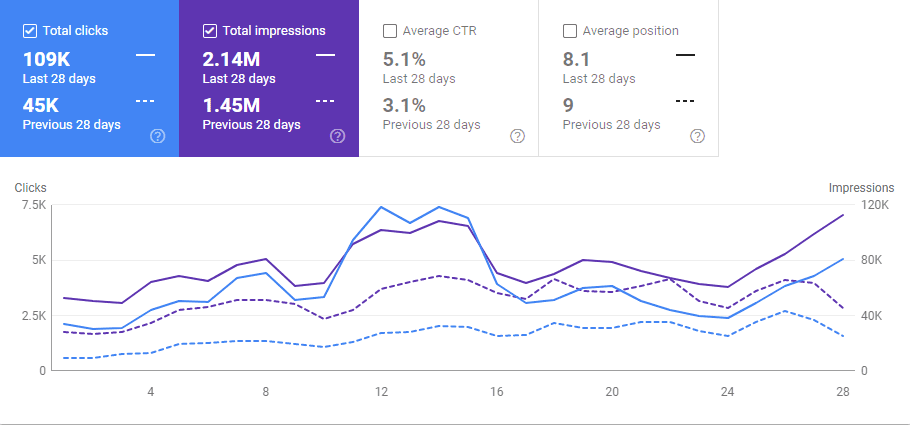
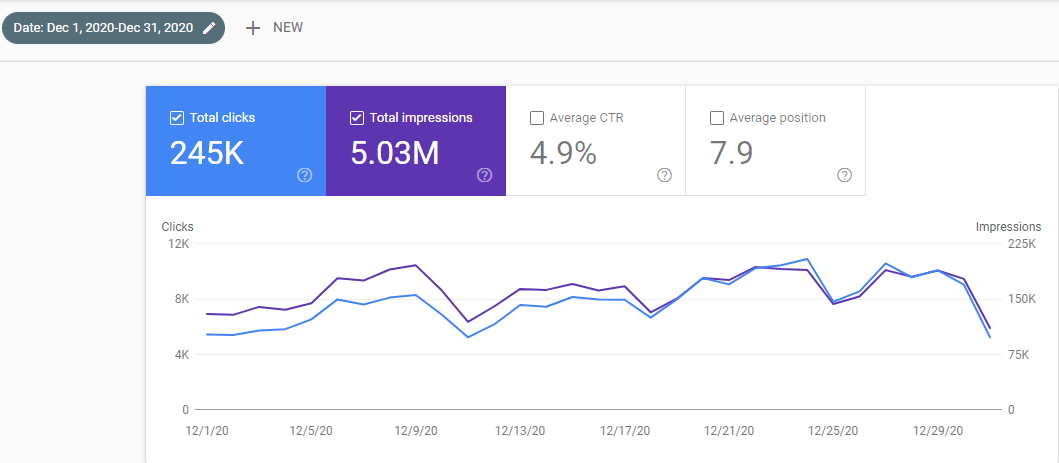
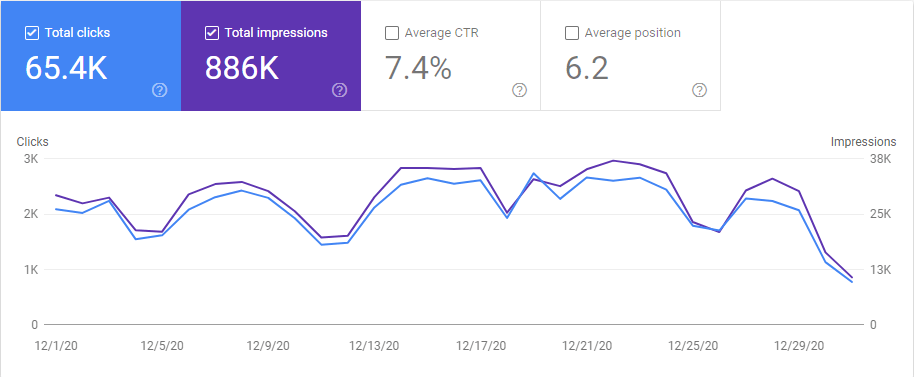
Below, you will se the Last 28 Day comparison from the 29th day of December.
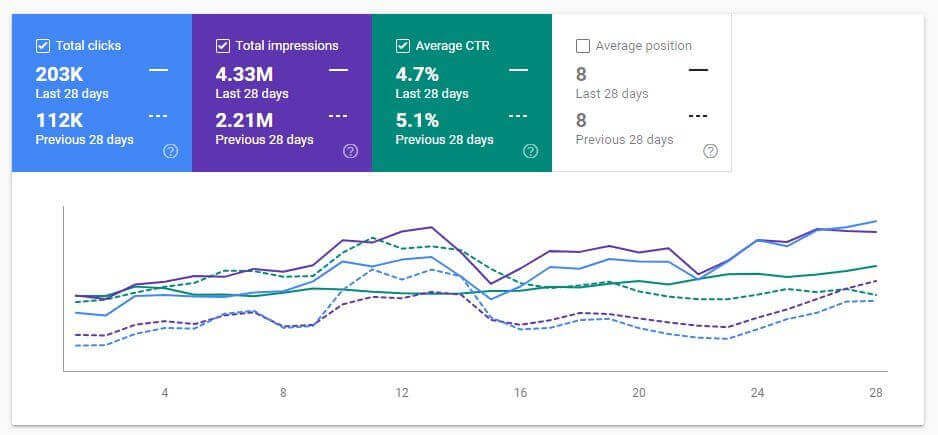
Below, you will see the Last 28 Days comparison from the 29th day of January.
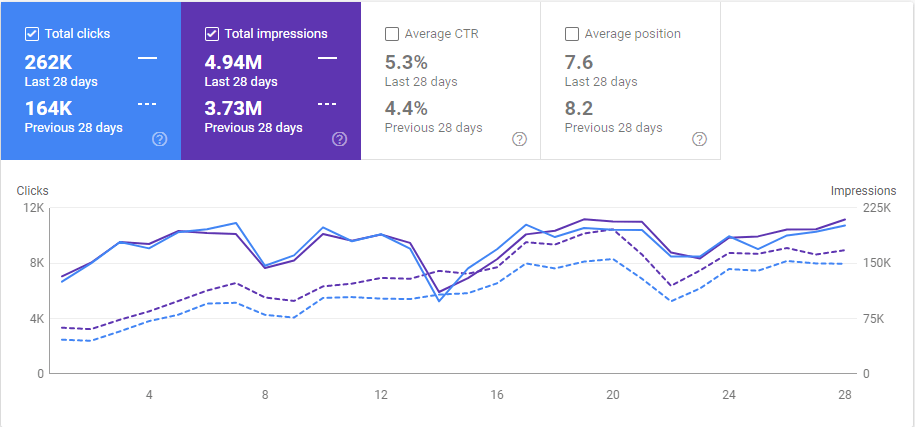
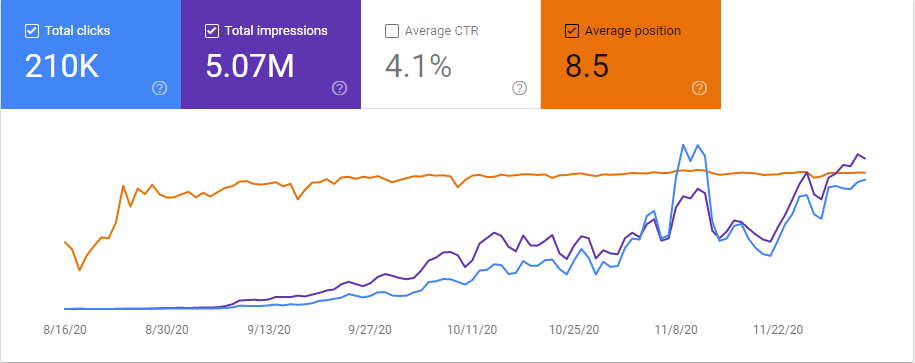
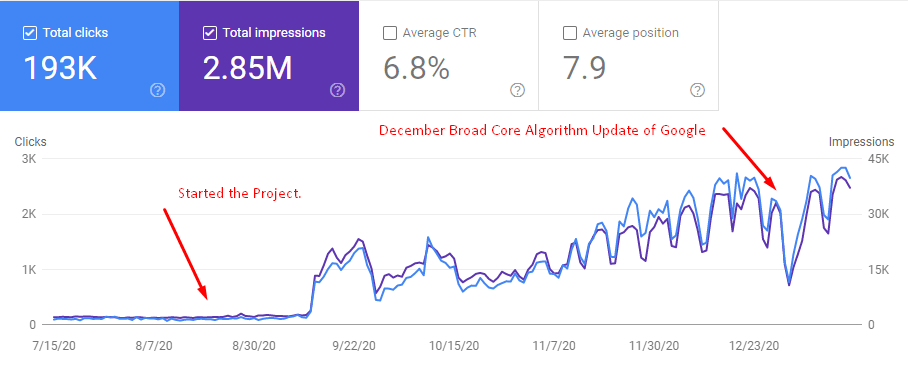
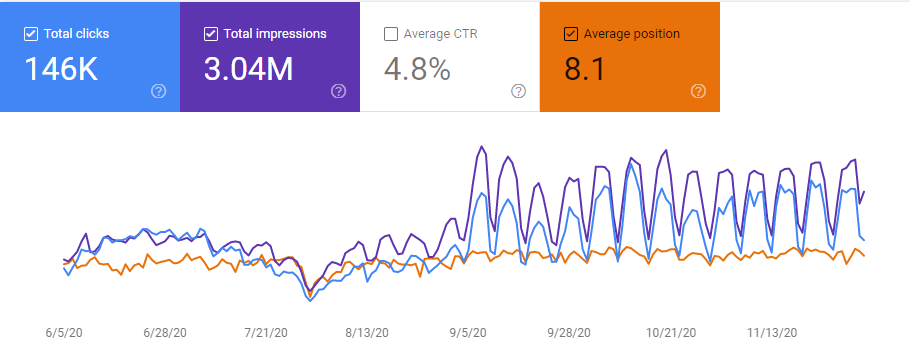
Below, you will see the last 6 month graphic from Google Search Console.
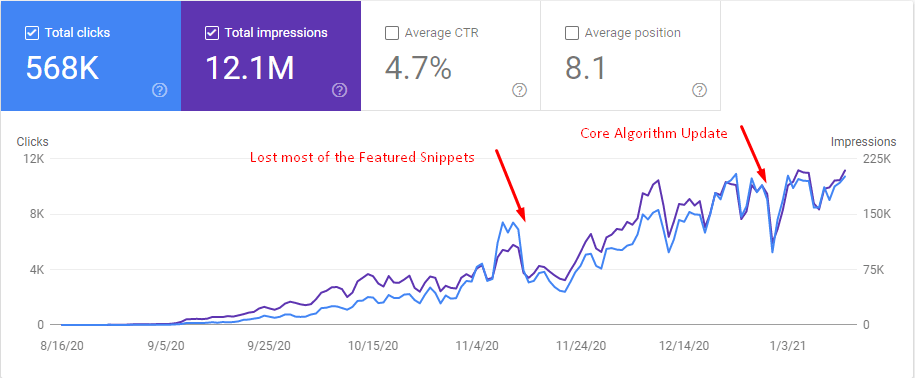
My main purpose with this SEO Project is actually 1 Million Organic Session in 12 Months. But, I am not sure whether I will be able to succeed after I lose these two minor Google Updates that are solely focused on Featured Snippets and possibly coming Passage Indexing (Ranking).
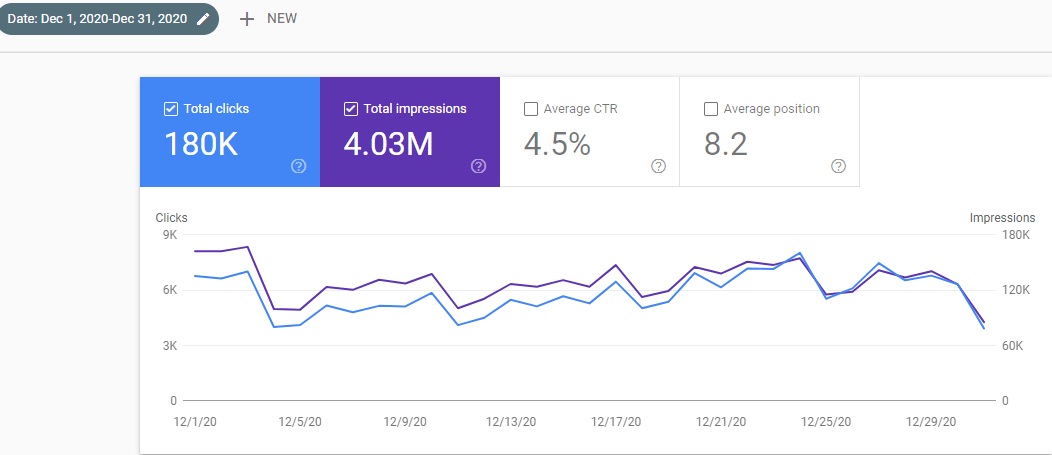
Below, you will see another screenshot from 6th of December 2020, 2 days after the December Core Algorithm Update.
We will show how Google tries to see the Possibility of User Satisfaction after a click and how a URL can be more authoritative and satisfying for the users and Google’s algorithm in terms of the information and function it contains.
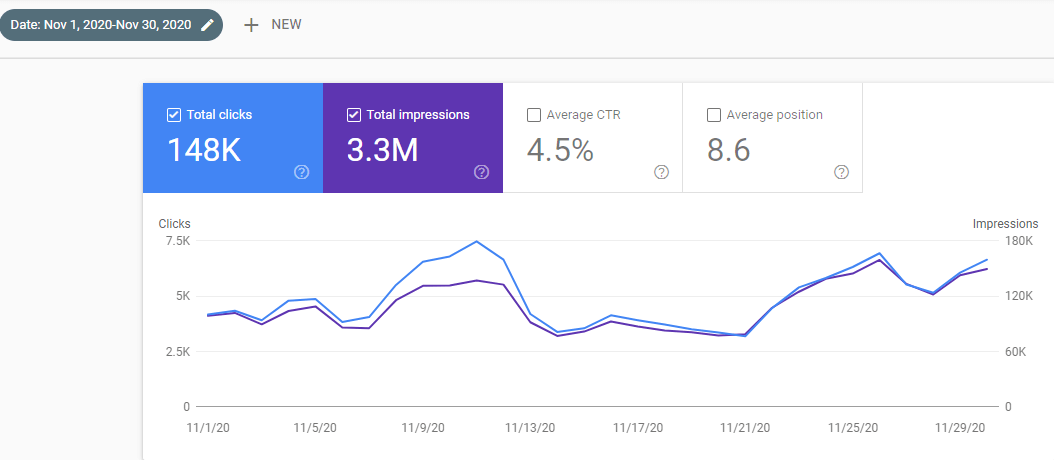
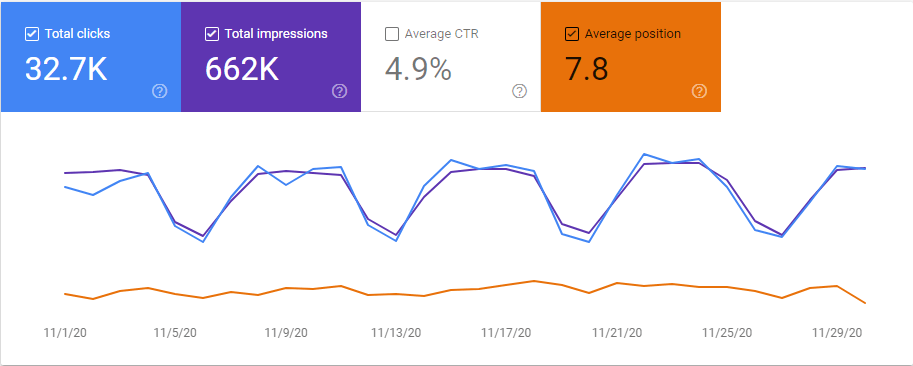
Below, you will see the graphic for all of November, 2020.
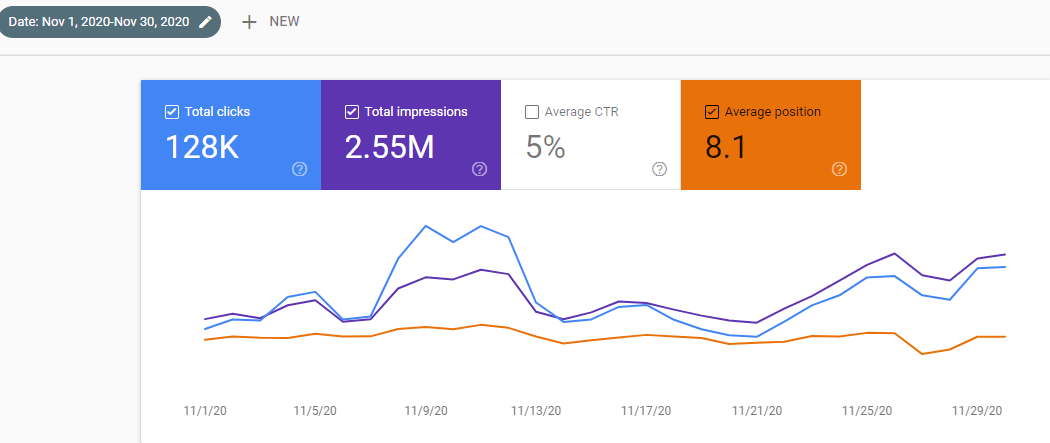
Below, you will see the December 2020 Organic Traffic Report from Google Search Console.
Before going further, let me introduce myself. My name is Koray Tuğberk GÜBÜR and I am a Holistic SEO Expert. I own an agency called Holistic SEO & Digital. I manage digital marketing campaigns with different aspects from Data Science, UX, CRO to SEO. In this SEO Case Study, I will mostly focus on SEO’s Theoretical Side’s true power on SERP.
At this point, I know you all have the same question on your mind. Normally, I would not give the name of the website as the aim of the project is 1 Million Organic Session Per Month and this SEO Project still continues to grow. But I got “as always” reasonable comments from Elias Dabbas, whom I see as a mentor.
That’s why I will explain the name of the domain. More importantly, “Most Prestigious SEO Crawler: OnCrawl Review ”, Google Search Console Data of the relevant domain, and all Technical SEO Analysis appears, you can review. So, you can see that I have achieved relevant success with a website with lots of errors only with “Semantic SEO” and SEO Theories/Patents.
The website (First Site) is called “Getwordly.com”. As you review it, as I said and explained during the article, all the Organic Traffic Growth success was born only from SEO Theories and Semantic SEO, not Technical SEO, Pagespeed Optimization or Brand Power or Advanced Layout design.
Who Should Read the SEO Case Study Based on Semantic SEO and Semantic Search Concepts?
This article mainly on Getwordly.com’s SEO Project and Case Study and Its Success is largely for experts familiar with advanced SEO Theories, Search Engine Patents, and Concepts. Therefore, the Executive Summary is at the end of the article. If you don’t have enough information or analytical thinking skills to understand a Search Engine’s perspective, you won’t understand the executive summary and the results that I manage to get, therefore I strongly recommend you to not read this article. And, read the second SEO Case Study article that is published on OnCrawl.com for mainly the “Second Site” which is Interingilizce.com that covers the same methodologies with a broader and brief Executive Summary.
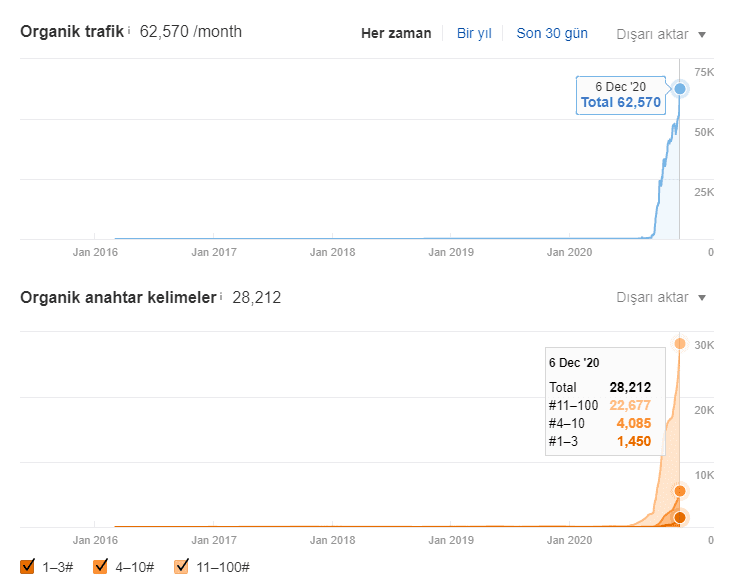
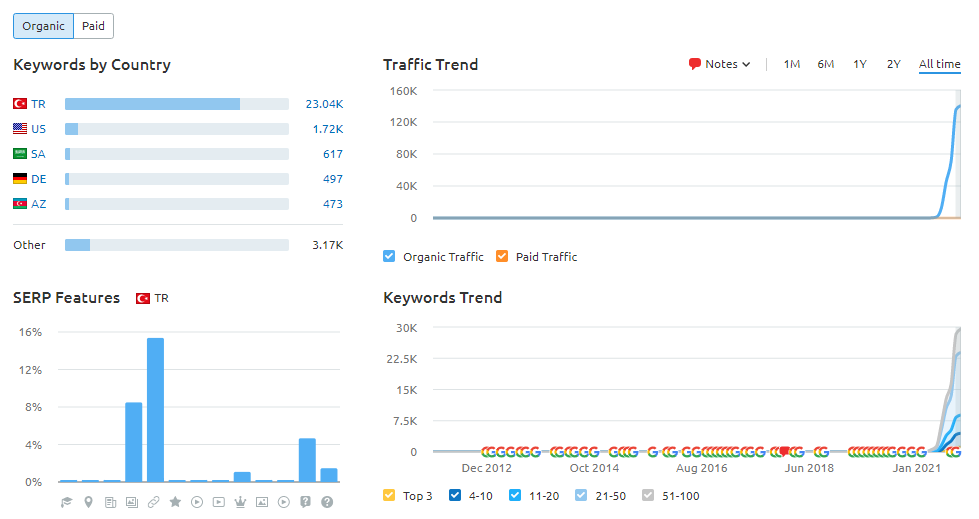
Below, you will see the last situation of the Getwordly.com’s Ahrefs Report.
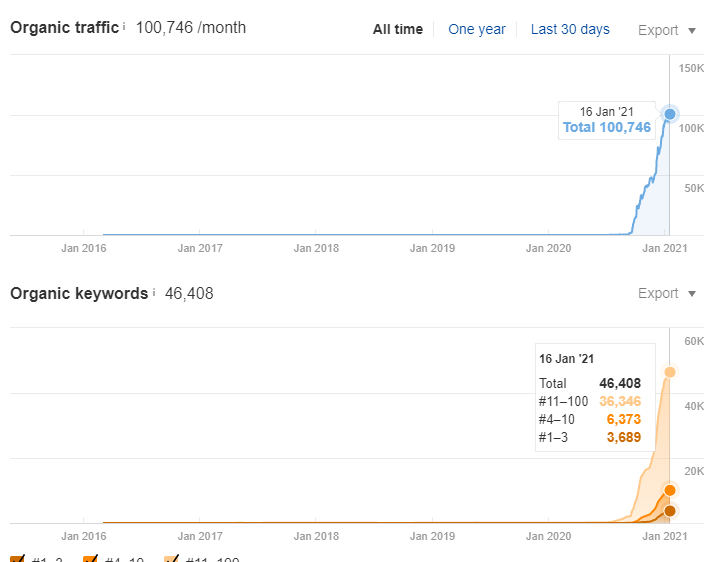
To show that the concepts in the article are working, I put the graphics of three more websites that I used the same methods and SEO Insight. However, I will explain the names of these sites in shorter and less detailed articles that I will write for regular readers, with their unique characteristics.
All three websites below are in the same SEO Project, in the same niche. Only the “target audience” of some varies depending on the geography.
200.000+ Organic Traffic Per Month in 6 Months: Interingilizce.com (Second Site)
The Second Site’s SEO Case Study is published on OnCrawl.com. If you are an average SEO or newbie in terms of “Search Engine Patents, Theories, and Terms”, I strongly recommend you to read Second Site’s SEO Case Study since it will be a more simplistic Executive Summary.
This site is only for “Turkish” and it is from the same niche. Thus, it has acquired the same traffic slower, because GetWordly.com is a multilanguage website. “Site 2’s” Semantic SEO Case Study will be published later with a more simple article for normal readers, later. You may see its organic growth thanks to SEO Knowledge and Semantic SEO, below.
Besides GetWordly.com, Site 2 which is Interingilizce.com:
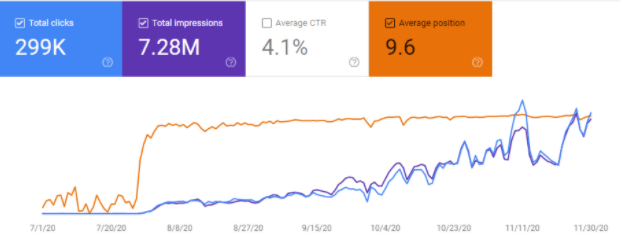
Below, you will see the last 5 months graphic with a broader aspect from the Interingilizce.com’s Google Search Console.
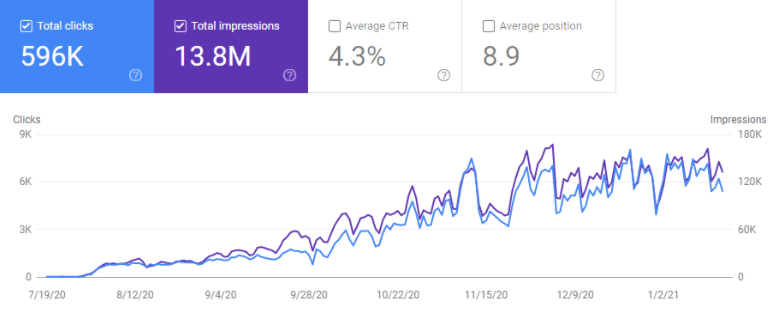
This is the graphic for the last 6 months. You may see the similarities between Getwordly.com and the “Site 2” which is Interingilizce.com, since they are from the same niche with the same methodology, it is a normal process. And, after the December Core Algorithm Update, I have lost the featured snippets again but it didn’t happen for Getwordly.com, at least yet.
Below, you will see the December 2020 Situation of the Second site in terms of Organic Search.
As you can see in the 6 months, we have acquired 180.000 Organic Traffic per Month. The Last 28 Days Comparison from the GSC below had been taken in the Middle of December 2020.
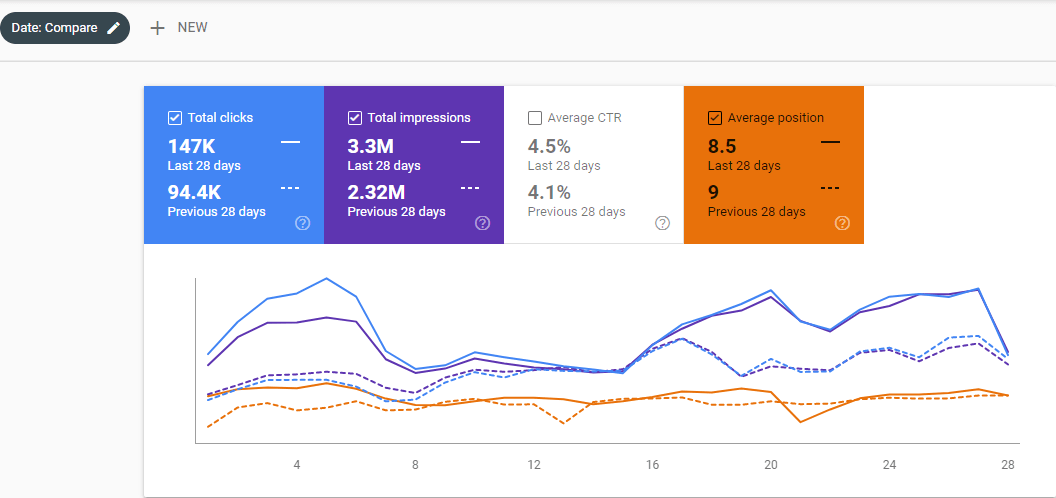
And this graphic above is for showing the Last 28 Days (From the Middle of December 2020) comparison. For every Semantic SEO Project based on SEO Theories, the organic traffic growth can be acquired in rising waves shape.
+7.000 Clicks per Day in 6 Months and Effects of a Real-World War on a SEO Project: Site 3
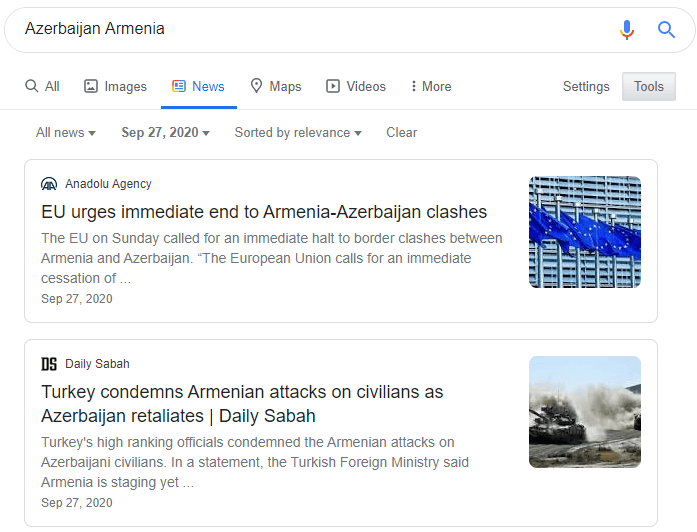
Unfortunately, we have seen a real-world war’s effect on an SEO Project with Site 3. The third site is also in the same niche, but it solely focuses on “Azerbaijan”. And the war between Azerbaijan and Armenia has shuttered the organic growth of Site 3. Since Azerbaijan has the only a Population of 10 Million, the Third Site can’t have such a big traffic increase organically.
You may see the “War’s Effect on the Website” below. The screenshot has ben taken in the 9/27/2020.
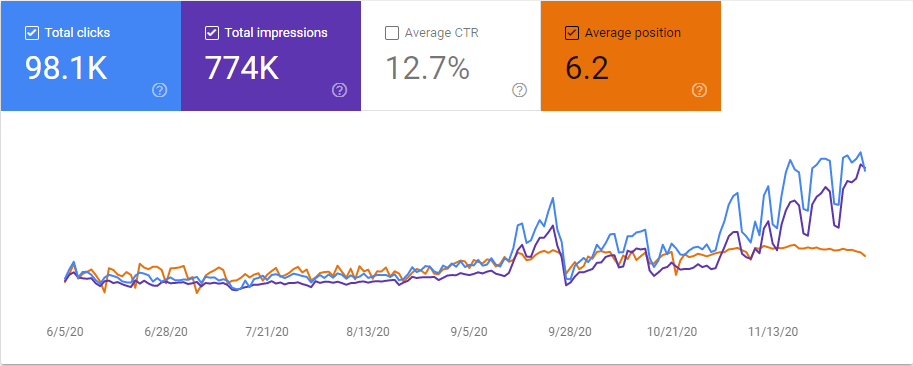
Below, you can see the valid situation for the Third Site’s SEO Journey.
Below, you will see the last situation of the Site 3’s SEO Performance for the SEO Case Study.
We have just started to gain organic traffic with the Third Site, but with the news of the War we have lost the gainings. But, I have a “assumption” here. We just didn’t lose the Organic Traffic, we have also lost the “Average Position”. I assume that “Google’s Algorithm Hierarchies” have started to trust the website with the sudden traffic loss, and it couldn’t understand the reason of the “search demand” and “user behavior” change, it has started to same process again.
During the war, we have seen the same graphic again and again, and whenever the war rages, the same graphic and event happen. Thus, I assumed that Google tries to see a website’s expertise and trustworthiness with historical data. And with the sudden Search Behavior shifts without an understandable reason, Google’s Algorithmic Hierarchy tried to start the same process again and again, that’s why we see the same rising graphic always.
Below, you will see the last 28 Days Comparison.
And, this is from November. This website isn’t affected negatively from the Google’s December Broad Core Algorithm Update in a permanent way.
Below, you will find the December 2020 Google Search Console Data for the third site.
Interesting Fluctuations and Cultural Differences for the Last Website:
The last and Fourth Website is only for the Arabic Countries. And, I believe, thanks to Cultural Differences, we see more “precise” and “concrete” fluctuations in the Organic Traffic Graphics, because all the “bottom points” of the Organic Traffic Graphic come across to the “Friday”. And, you also can see that since in “Fridays” we don’t have “search demand” and “search behavior”, we also lose “Average Position”. When Search Demand increases, our Average Position also increases.
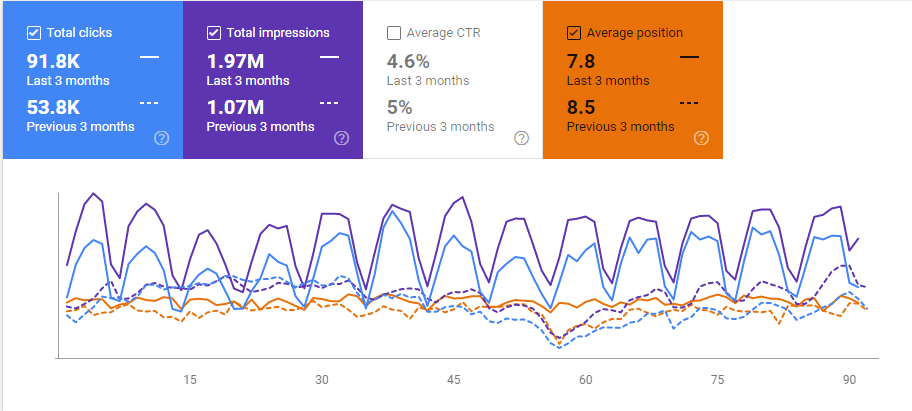
This is consistent with our “Azerbaijan” Example. If your website doesn’t have enough historical data and brand power, or if you have lots of missing Technical SEO, Pagespeed and Layout improvements, these types of switches can affect you more. Below, you will see the graphic for the last 6 months.
And, this is the last 3 months comparison of the Fourth Site.
After showing the all results from the same SEO Project with 4 different sizes for the four different geographies and target market, the background of these SEO Cases can be seen clearly.
During this SEO Case Study, Technical SEO, On-Page Optimization, Web Page Loading Time Optimization and Branding are not being performed or implemented so that we could see only the power of the Topical Graphs and Knowledge Domain Coverage Effects in a given search query and search intent group.
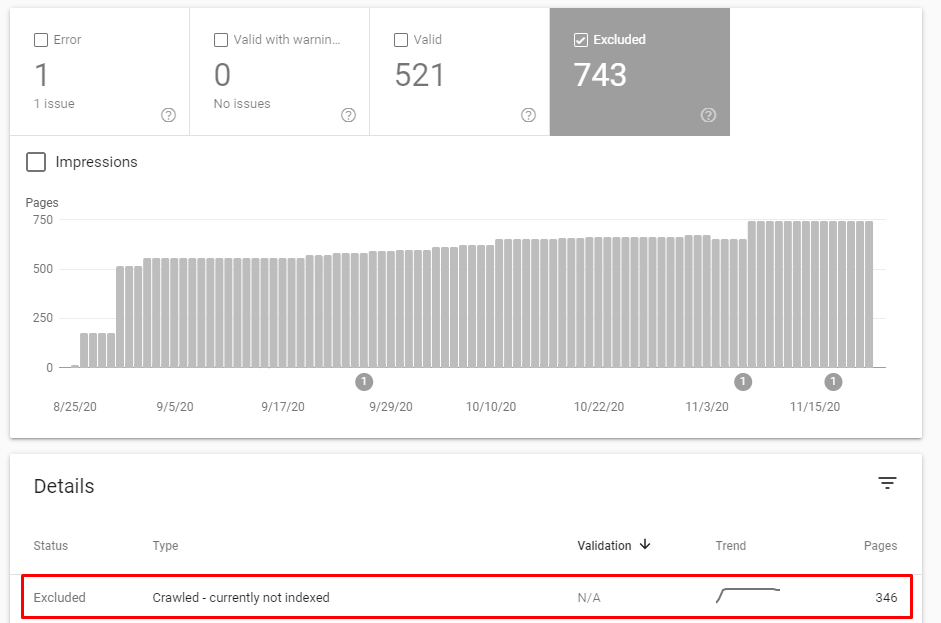
And, when I completed the SEO Case Study, I had 346 web pages that are waiting to be indexed, so you can see the Negative Effect of Lackness of Technical SEO.
Also, terms and theories from the Google Patents will be explained along with the negative effect of lackness of Technical SEO and other absent methodologies in this SEO Project, so that the value of “actionable” information from the Google Patents can be seen better.
For instance, this website is a multi-language website for three different languages, but for the first 60 days, I didn’t even use the “hreflang” tag. And, I will show what is “PageRank, Relevance and Authority Sharing effect” of hreflang tags with the result that comes after I add them.
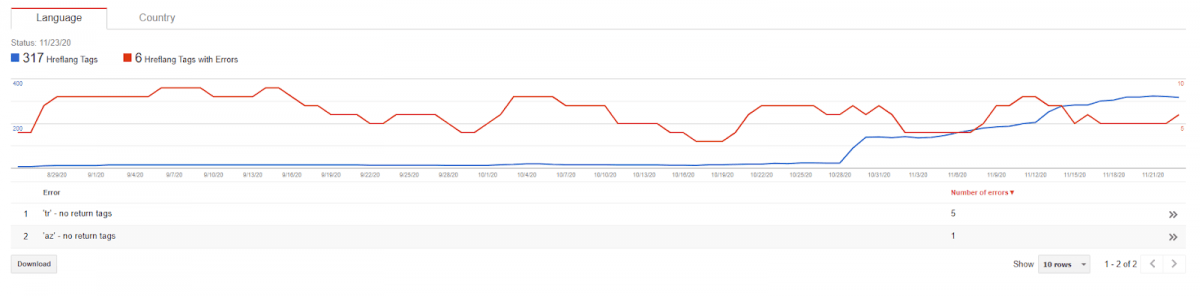
This is the current situation of hreflang tags, as you might see, it is not being used for the beginning phase of the case study. And, you will see its positive effect after I implement them, as I said.
And, in this SEO Case Study, the “header menu” and “footer menu” didn’t exist. The sidebar had only 5 links that point to the latest articles. Average Link number for a web page was just 10. 5 of them were in the sidebar, one is at the footer for homepage, one is in the header for homepage and 3 of them are in the main content with contextual relevance within a topical hierarchy.
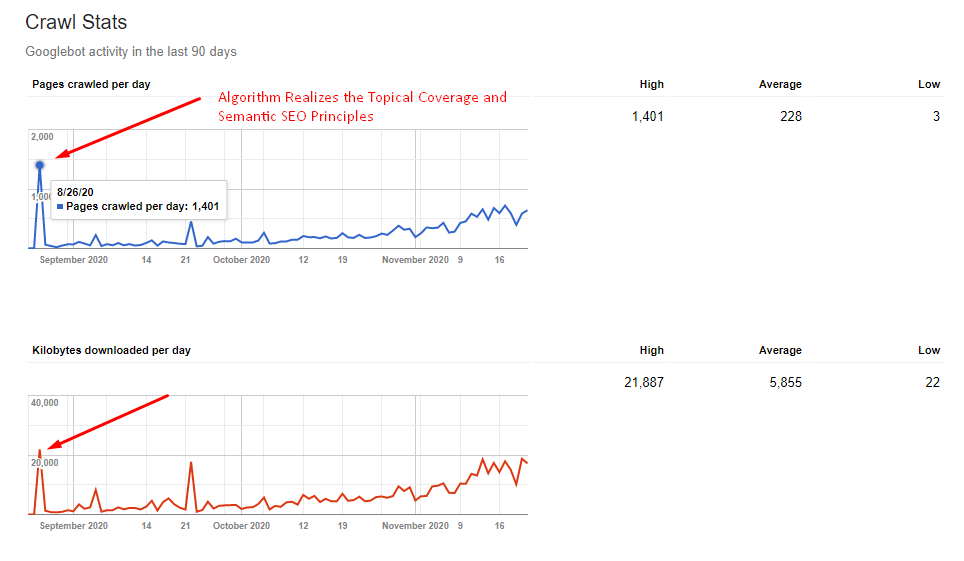
After the 28 September, Tuesday, Google has increased the Crawl Budget of the Web Site. It crawled more than 1400 Pages (more hits for some pages), and we started to see consistent improvements.
Also, we didn’t have a strong server or strong “design” and web page layout. So, basically, besides the content structure, network, and SEO Theories, we have nothing special in this success.
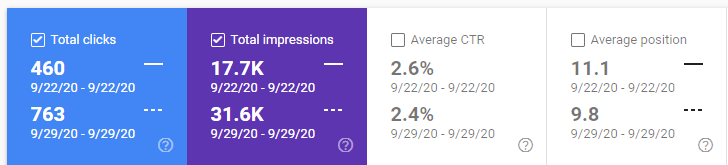
This is the comparison between 29 September and 22 September. Both of these days are Tuesday. After 28 September, The Web Site has been noticed by the algorithm with its expertise and Topical Consolidation.
Let’s start telling the actual story, first SEO Theories and Terms from Google Patents that created my vision:
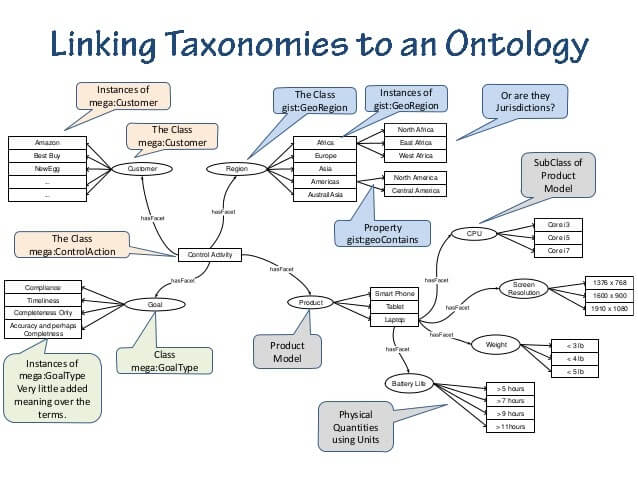
What are the Knowledge Domains
Knowledge Domains are the domains of specific queries, entities, layout designs, search patterns, and user segments. A Knowledge Domain has specific information, layout design, sentence-information structure, and also user-satisfaction model.
For instance, in the Currency Knowledge Domain, a high bounce rate can be a good thing, a bad page layout also may not be important. Because most of the users will only look at the current exchange rate and then they will bounce. This means that they do not need a long session duration or a fancy layout.
In a Knowledge Domain, Google or other Search Engines might classify the content publishers and service providers according to their speciality, authority and coverage along with their sum of historical data. They can unify different information sources from “Gmail” to “Chrome” or “Social Media Activity” to understand the situation of the Source, for the specific Knowledge Domain.
A Knowledge Domain can include “experts”, “apprentice” and “laypersons” based on the Information and Service Sources’ expertise and organization level. For all of my SEO Case Studies, Bill Slawski and his Search Engine Patent Analysis in the size of an ocean have a special place. You may read the article below to see more about Knowledge Domains.
Website Representation Vectors to Classify Expertise and Authority by Bill Slawski.
Also, If you want to take high rankings from a Search Engine beyond 2020, you should be aware of what the Complex Adaptive System is.
What is the Complex Adaptive System?
A complex adaptive system is the whole of a hierarchical and semantic signal and meaning network. The meaning and context of the whole are way more complicated than individual systems. I call this as “Uncertainty Principles of the Search Engines” and “Algorithmic Hierarchy” of the Search Engines.
In the old days, when Information Retrieval was the heart of Search Engine Algorithms, nothing was complex or adaptive. It was a simple “if and else” system with certain commands and score calculations. For instance:
- “If there is “string” in the title tag of the web page, relevance score will be increased Y Percent.”
- “If the “string” match case exists too much, increase the spam score Y*2 percent”.
- “If the spam score is higher than the relevance score, neutralize the web page’s relevance and historical data for the given queries”.
In this example, we see an example of the Information Retrieval Model, it basically takes certain decisions under the “non-complex” information along with “string searching” in the document.
But also, you will see that even this simple algorithm has a “Hierarchy” in it. It says that “do that, under this condition, but also if another thing exists then cancel the previous decision”.
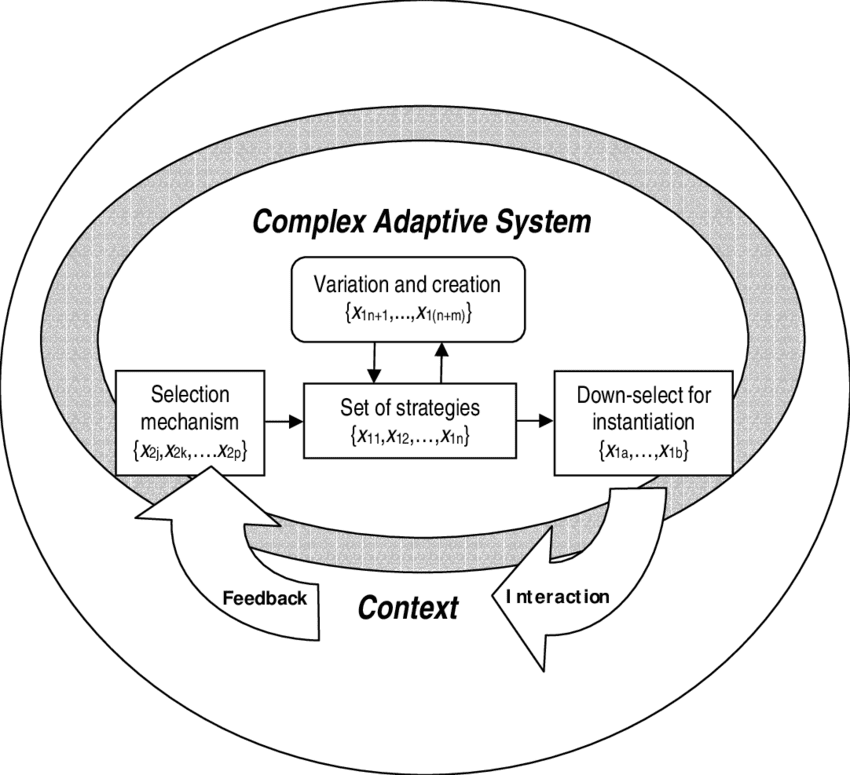
Now, let me explain the Uncertainty Principle of Search Engines in the context of the Complex Adaptive System.
Uncertainty Principle and Complex Adaptive System
Google is a hybrid search engine with lots of parallel conditions, features, and abilities, it can collect real-world data, extract information and facts from the large web corpus, it can recognize entities and entity connections, analyze the sentiment, expertise, and the users’ satisfaction possibilities along with the spam activities via its millions of algorithms within a certain hierarchy.
The Complex Adaptive System moves in this specific section. Google doesn’t give its decisions suddenly with only two or three simple metrics that are easy to be manipulated or perceived.
Instead, it seeks consistency within the metrics related to the brand entities to take their decisions. These decisions can be made with the approval of millions of algorithms in a hierarchy. None of these approvals create change suddenly, instead, they change the SERP bit by bit, also sometimes the spam detection algorithms may try to see that the brand entity is making spam or not by changing the rankings for seeking a reaction from the brand owners.

In this context, the Complex Adaptive System is the methodology of Google to see a consistent improvement in every ranking and quality, reputation, and trust signals all over the web. From search demand, news, mentions to code structure and coding errors, or design improvements, all of them are in the system before during the decision-making process.
In short, every byte, pixel, letter works in harmony in the Search Ecosystem for creating the final ranking landscape. Below, you will see another Google Patent Term that creates this SEO Case Study and help us.
What are the Context Vectors?
Context vectors are the vectors that are used for determining the context of the content or content publisher in given search intent. Google simply tries to profile the words that are being used in a certain domain to see what are the unique sides of a context.
This can help Google to see the difference between different contextual domains so it can also differentiate the characteristics of the different user-behaviors, expectations, and “quality parameters”.
For instance, a quality parameter in a certain section of the web can be a non-quality signal in another section. For instance, even if you write really detailed, unique, scientific, and great articles, it can’t be “quality” because of the expectations of the users. If it is too long, people may skip most of the article without seeing the actual answer. Thus, even if you would be in the correct contextual domain, Google can see that for the given context, people may prefer more “fast-food” style content.
For instance, WebMD experienced such a problem during the core algorithm updates, last year.
You may try to understand your context vectors by selecting unique words, terms, concepts, and phrased for the given contextual domain.

After the Contextual Domain, Knowledge Domain, Uncertainty Principle of Search Engines, and Complex Adaptive System, we have another SEO Theory term called “Contextual Hierarchy.”
What is the Contextual Hierarchy?
Contextual Hierarchy or the Conceptual Hierarchy is the hierarchy between different contextual web sections. For instance, a search term, search intent, or sensitivity-metric can be unique for a given context and also its sub-contexts. Seeking a flight ticket can have multiple sub-intents such as “seeking a flight ticket for holidays or business meetings? Or just seeking a flight ticket for making a comparison between the prices between the brands or time spaces?
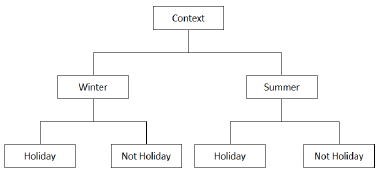
For instance, you can see another Contextual Hierarchy visualization here based on different periods of a year for just a certain “search intent” which is holidays.
In light of this conceptual hierarchy, there can be mutual and also different search terms or phrases for the given sub-intents and search behaviors.
These sub-intents and search term matching create the contextual and conceptual hierarchy. Imagine there are different contextual zones in different verticals and also horizontals. Google profiles these contextual zones along with the search terms, search results expectations, and content-publishers’ quality parameters.
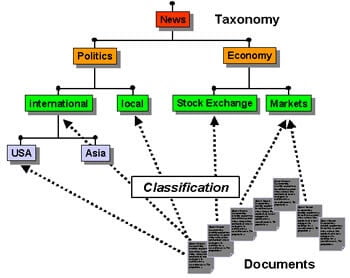
What is the Topical Graph?
The topical Graph is the graph of the corner-stones of a topic. Questions of “how, what, who, where” and their answers are the cornerstones of a topic. Answers to those questions, information of those answers, things in these answers, and related terms, phrases, concepts create the general aspect of a topical graph.
To create a topical graph, you should use the Semantic Search Mindset along with Semantic SEO Principles. Every topic and every sub-topic and every micro-topic are connected to each other in a certain Contextual Hierarchy in a Knowledge Domain with certain quality scores of content publishers and user-satisfaction possibility.
Below, you will see an official video from Google Developers. When I saw this video for the first time, I came up with the term “Search Engine Communication” and “Semantic SEO”. The latter has started to become a popular concept in the field of Search Engine Optimization. The first one is actually my own invention.
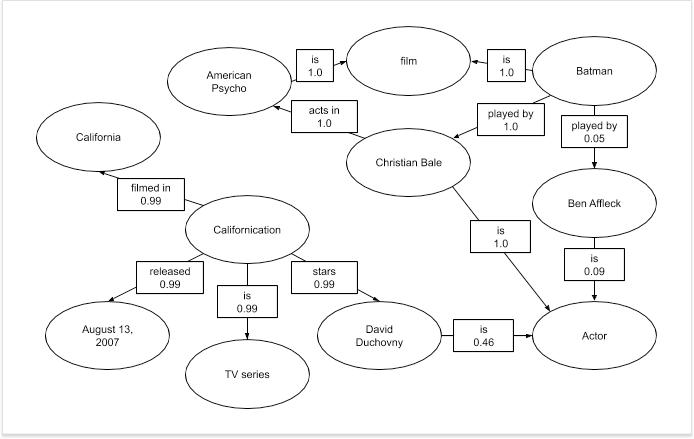
What are the Entity Connections?
Entity Connections are the connections between different entities in a given context. A thing can be a family member of another thing or a thing can be a song of another thing. Things or entities have different attributes that connect each other. These connections or attributes create a better context comprehension and improve the Search Engine Results Pages.
Entities are real-world existences with real-world data. Google may recognize, profile, and analyze an entity and improve its own Knowledge Base.
Entities and their descriptions, types, links (Named Entity Links), attributes can create a real-world comprehension for the Search Engine and it can help the Search Engines to see a brand-entity’s authority, coverage, and historical data for a given entity.
Thanks to entity-seeking queries, the search engine can profile a specific user segments’ behavior, expectations.
Also, including an entity’s related attributes and also related phrases, queries, and topical graphs into a related article with a contextual hierarchy is the key here for our content marketing strategy.
What is Neural Matching for Google?
Neural Matching is a technology where Google combines different queries under the same search intent with the help of Neural Network and Neural Embedding and matches the meaning of the term in the content of the user’s query by taking similar web pages into the same cluster.
Google first described this concept in 2018 with the example of Danny Sullivan’s “Soap Opera Effect”.

Two years later, Google used the same concept once again with the title “How AI is powering a more helpful Google”.

In other words, Neural Matching is the “Query Term Weighting” operation in the “Query Processing” process by understanding the concept in the user’s query according to the context of the user’s query, and matching the same term within the scope of the same context and the same search intent in the documents to be included in the search results.
What are Neural Nets for Google?
Neural Nets is another concept related to Neural Matching and refers to the concept of “topical hierarchy”. Accordingly, the search intent determined by Neural Matching is located in a topical hierarchy, within a sub-topic. While the context of a user query is affected by the query intent, Neural Nets are a combination of different sides and sub-topics that cover all of these intents and contexts.
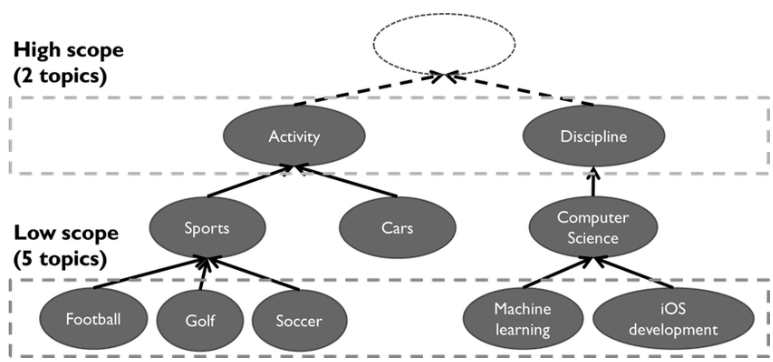
Neural Nets and Neural Matching concept is important for Topical Coverage and Topical Authority that can be obtained in Semantic SEO studies. To cover every related Neural Nets (Sub-topics), Contexts, and Search Intents within a Semantic Content Network with contextual anchor texts and quality content that contains all related entities is the important methodology here. You also can see some topical categories in Google’s Natural Language Processing API as below.
See the full list of Content Categories in Google’s NLP API.
What is a Unique Information Gain Score?
Unique Information Gain Score, or simply Information Gain Score, is another concept from Google’s patents that directly concerns SEO. Information Gain Score allows you to examine different contents and Information Sources to measure which one can gain more information to a person.
In this context, the Unique Information Gain Score is a score for calculating the unique information amount within a content according to its competitors. It is not enough for content to be original. At the same time, he should convey the questions that his competitors cannot answer, the questions he did not answer, in the correct content format, with the least words and the most information.
A search engine can calculate the information gain score based on contextual search intents and users’ preferences along with the content-based differences. Also, “semantic representation of words, feature vectors, a histogram” can be used with machine learning to calculate Information Gain Score.
What is “Question Generation” from Content?
Question generation is actually not a new term for SEOs. Since the first day of the “People also ask” SERP Feature, we are aware that Google doesn’t scrape questions from content, they actually generate questions and choose the best candidate passage from the candidate documents.
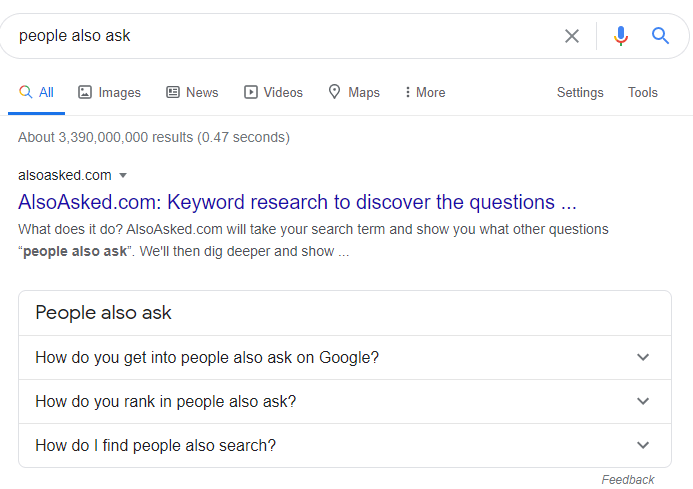
People Also Ask questions don’t exist in the content of the web page as a “phrase”. Google usually chooses a Candidate Answer Passage from the content and then generates the related question from the content. For instance, I will open the first question from the People Also deck in the image.
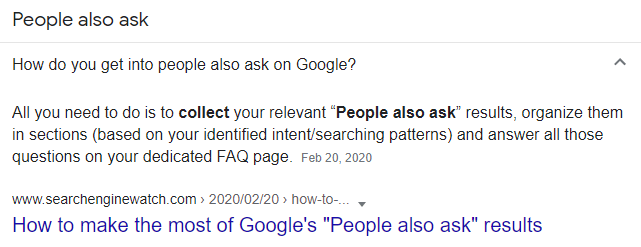
Search Engine Watch and an Answer Passage has been chosen as the answer here.
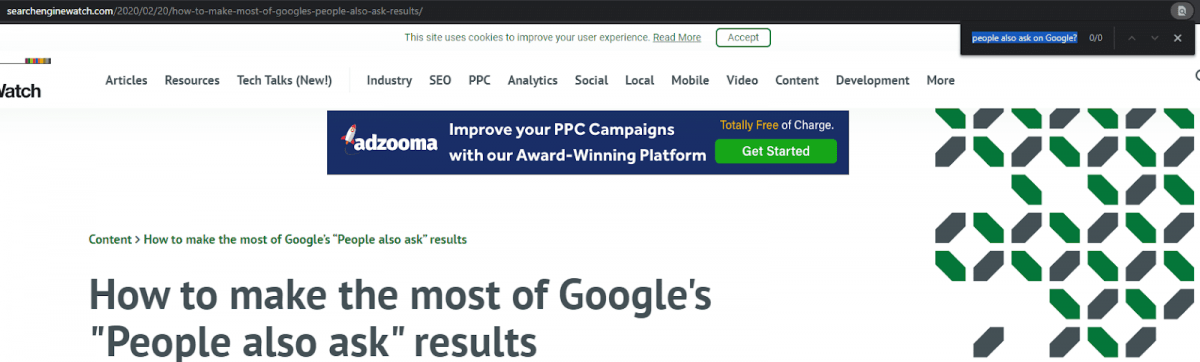
When I enter the page and search for the question, I can’t find the exact match of string here. Actually, even there is not a similar question on the web page in terms of “phrase shape”. Google, collect all similar search queries from the users for certain Neural Nets and Contexts. Then, Google generates questions from these queries and chooses the best candidate answers from the most relevant and authoritative web pages within a Knowledge Domain.
Entity connections, Topical Coverage, Topical Authority and more are real-world actors here as more than just theoretical terms.
And, you can check the Google Patent below for “Generating Questions”.
Why is “Question Generation from Content” important for our SEO Case Study?
Because, while creating the content network, I have generated questions, collected questions, scraped questions and populated questions within a semantic structure to create the best possible “Unique Information Gain Score”.
What is “Heading Vectors” for Google?
Heading Vectors and Contextual Vectors are similar terms to each other. Contextual Vectors can be used within a Knowledge Domain for specifying the special terms for that interest group. But also Heading Vectors can be used for determining the context of the passage under a heading within the main content of the web page.
Heading Vectors is actually a term from Google’s “Context scoring adjustments for answer passages” patent. It is being used for determining the best possible “Candidate Answer Passage” for a question. For instance, if someone asks for “What is the definition of Morphology”, the heading vectors should contain a relevant contextual hierarchy within each other.
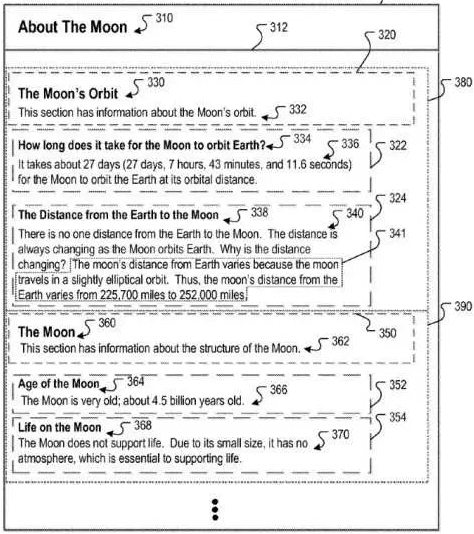
If the Root Tag (Title Tag) of the content is “Less Known Terms from Greek Mythology”, and the most relevant heading within the content is “Morphologic Creatures from the Greek Mythology”, the heading vector and its context might signal that this content might not be the best candidate for this query. If the Root Tag is “Everything about Morphology”, and then if there is a heading tag as “Morphology and Its Importance in Language” with another subheading as “Meaning of Morphology”, the Heading Vector and its context might signal that this is a better contextual journey for the Candidate Answer.
Why is “Heading Vectors” important for our SEO Case Study?
Because, after generating tons of long-form content that has lots of generated related and semantic questions, I need to create a “Heading Vector” for protecting the context of every content within a Neural Net for different Sub-intents. Every sub-intent and a candidate answer passage for the queries of that sub-intent should be organized within a hierarchy according to the search intents’ domination to each other and contextual relevance.
In other words, I need to organize the generated questions from the content sections with a logical hierarchy.
What are the Link Types for a Search Engine?
Links on a web page can differentiate in terms of their true value according to their text, position, style, color, clickability, and distinctively on the web page. Every link on the web page has a different meaning. At the moment, we know that Google uses PageRank (even if they say, we don’t use PageRank, I am afraid that I wouldn’t believe them), but we don’t know which PageRank calculation model that Google uses. So, to convey the best possible relevance and authority between two web pages, link amount and link position are the most critical factors along with link text.
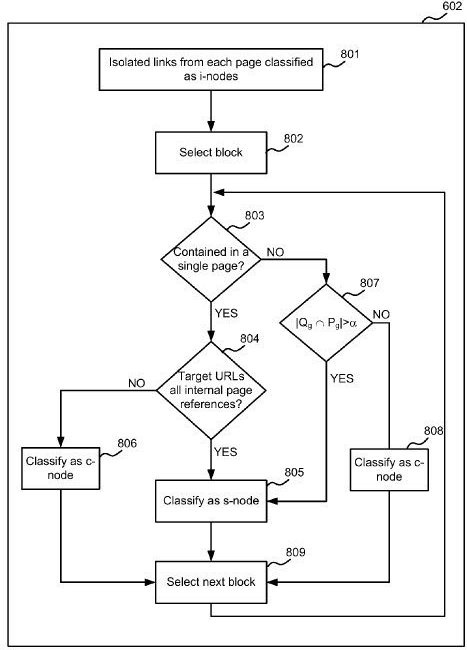
Below, you will see how Google might classify links on a web page.
- Locality: Difference between local and global linking structure of a website.
- Completeness: Contextual and logical navigational structure on a website.
- Scalability: Differences between Block and Individual Links.
- S-nodes: S-nodes Links are the links that repeated across different web pages for organizational navigation.
- C-nodes: C-Nodes links are the block links within the main content of the web pages.
- I-nodes: I-nodes are the links that individual links without similar neighbors. I-nodes links have the highest contextual relevance between web pages.
Understanding Link Types in the perspective of Google Search Quality Team with their possible terminology can help for SEO.
Why is “Link Types” important?
In Our Case Study, we have used only “3 Main Content Links” with anchor texts.
These links had the exact match main query within them.
Annotation Text and Anchor Text were adjusted for search intent of the user.
In other words, I used mostly “I-nodes Links” in this SEO Project. The Sidebar Links were for only the latest 5 content. Footer and Header Links are just for Homepage since it is clearly stated that having links for homepage within the footer and header is important in Search Quality Rater Guidelines of Google.
Thus, I have used 200% fewer links according to my competitors within my website.
Most of these links were in main content and they have relevance for the user and Contextual Hierarchy.
What is Update Score for Google?
Update Score is actually a term for “Query Deserves Freshness”. In Google Patents, there are three different terms that are related to each other.
Update Frequency, Update Amount and Update Score. You may see the relation between these terms below.
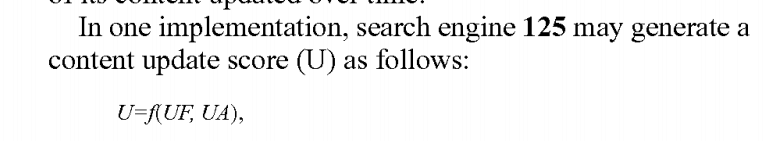
The formula says that “Update Score = Update Frequency, Update Amount. You may see below.

The patent name is “Document Scoring Based on Document Content Update”. In this patent Google tries to find a balance between freshness of content and prominence of source along with “diversity of content”. The update score also is not just related to the “updating of the individual content”. If you update a content, it will affect the most related and linked content within the same document network (source, domain).
Why is “Content Update Score” important?
After publishing our articles, I always make our authors update the content based on the initial ranking of the web page. Also, in some content blocks, I couldn’t add anchor texts for the relevant contents because the relevant contents were not published at that time. So, when I publish an article, I always check whether there is an anchor text waiting to be linked to that specific web page from a specific context.
What is Content Publishing Frequency?
Content publishing frequency is a similar term for the content update frequency. Both of these terms affect the Crawl Demand and Crawl Frequency of a web site. If Googlebot finds better content and more quality content in terms of the amount between different crawl processes, Googlebot’s machine learning system will give priority to your website according to your competitors. Thus, publishing content within a certain increasing frequency is important to provide this crawl demand and crawl frequency increase along with convincing Google’s Crawl Resource Organization systems to give priority to your website.
Why is “Content Publishing Frequency” important?
At the beginning of the SEO Project, I have only published 1 article in every three days.
After 20 days. I have published 1 article every two days.
After 10 days, I have started to publish 1 article everyday.
And in some days, I have published more than 1 article.
After 20 days, I have started to publish 3 articles a day. (Including, alternate versions for different languages.)
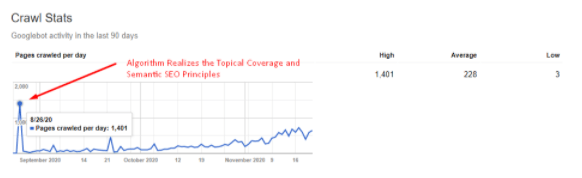
Also, since this is a multi-language SEO Project, I actually published 1 canonical and 2 alternate articles a day. Thus, you should remember the “Crawl Stats” graphic at the beginning of this SEO Case Study, after 8/26/2020, Google noticed my consistency and allocated more crawl resources.
This is also important since I didn’t use any kind of Technical SEO Methodology or Pagespeed Opt. in this SEO Project. Google knows when I will publish a new content and when I will update a content with which frequency.
What is the Content Format for Semantic Search Engine?
Semantic Search Engine organizes things on the web according to their types, attributes, and definitive meanings. An organized web structure also requires certain types of content format related to the certain type of entities and their query types.
For instance: An entity Comparison can include a certain type of content with a certain type of words. Such as “best”, “faster”, “bigger”, “cheaper”, “fresher”, “better”. Also, it can include HTML Tables or “lists”. After a while, the Semantic Search Engine can decide in which queries a list or HTML table should be shown or used on the featured snippet.
Thus, according to Semantic Search Engine, every content should be formatted for its context and the queries and questions that it tries to satisfy. Content can contain a list, table, or a definitive paragraph, and the following sentence that contains an example can be used. The author can tell his/her own experiences or the sentence should strip off from subjectivity. Sentences’ structure and grammar rules even can change according to their context and Semantic Search Engine’s perception.

Why is Content Format important?
During the SEO Case Study, I have formatted every content network piece according to its context. All of the “Differences” and “Groups” articles have included a list after a definitive sentence that defines the list. All of the “symptoms”, “methods”, “how-to”, “what are”, “educational content” and more are formatted according to these rules.
I have educated all of the authors on when to write what with which style and grammar rules within this concept.
As I said before, this SEO Project is based on “English Learning”. The educational perspective, concepts, and style along with Search Engine’s SERP Design and Feature preferences are observed and used for content format choosing.
And, all of this SEO Project is being built on Featured Snippet Hunting.
What is the Importance of Content Length?
This is a subsection for Content Format. I have only two rules for content length.
- Content should be as short as possible.
- Content should be as long as necessary.
Usually, I have made Authors trim the articles and told them “tell the same thing with lesser words but include the necessary entities and their connections with a descriptive and unique way”.
What is the Importance of Natural Language Processing for SEO Projects?
You may not know Natural Language Processing but after I have read Bill Slawski’s “Candidate Passage Answer Scoring” articles I thought that I am glad to learn Natural Language Processing terms and Python Libraries like NLTK and Spacy.
Natural Language Processing means that machines can understand an article like a human. Before the BERT Algorithm (DeepRank), instead of understanding a content, it was trying to understand the level of expertise and relevance of the content by noticing the entities in the sentence with “Named Entity Recognition”. However, with BERT, Google can see how the concepts are interconnected in a sentence, as well as understanding whether a content actually contains expertise or not, and can see content standards in a specific Knowledge Domain from different angles with Neural Networks.
I believe, with time Natural Language Processing Terms will be prominent terms for Search Engine Optimization.
For this SEO Project, I have educated the authors with NLP Terms, and told them why we are writing what reason within which style. I have taught them the difference between a query and an entity along with what I mean within the article briefs while determining the headings, heading vectors, annotation texts, anchor texts, methodology, and structure of sentences. And, I taught them where to use lists, where to use tables, where to use which “types of entities” and with which type of sentence structure.
What is the Dependency Tree?
Dependency Tree is the interpretation of every word in a sentence as an acyclic graph. Each word is linked to one another in a certain semantic relationship, changing the context of the word and contributing to its meaning. The words in a sentence are the nodes and the meaning modifications between them are the edges.
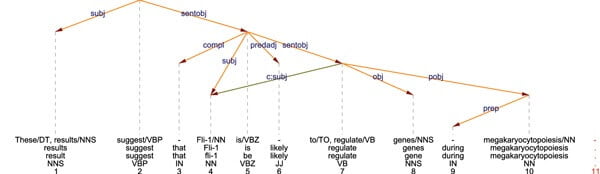
Why is the Dependency Tree important?
If a sentence is too long, the dependency tree also will be long and the meaning between the word connections will be diluted. From Cindy Krum’s “Entity-first Indexing” Article Series, I know that Google uses its Language Capabilities also in Google Translate. You will notice that Google is better at translating shorter sentences according to the longer sentences.
If you keep your Dependency Tree short, you will notice that you actually give “one piece of information” per sentence. In other words, answer one question “clearly” with every sentence. I have taught these kinds of perspectives to my author team during the article briefs so that they can avoid “complex, long and exhausting” sentences.
Note: If you use Google’s Natural Language API, you will see that it can detect more entities from shorter sentences.
What is Part of Speech Tag?
According to the Dependency Tree, words are tagged by Natural Language Processing technologies within their context and type. Sometimes, understanding a word’s context is not easy. A Search Engine can use phrase-based occurrence correlations such as “Word2Vec” to understand the word’s context.
For example, according to Hidden Markov Models, if the word “the” is used in an article, the next word is probably a noun by 40% probability, an adjective with 20% probability, a number with 20% probability. Thus, when the word “can” comes after the word “the”, it can be understood that it is used in a sentence as an object, not a modal verb.
Such sequences appeared to occur not only in “N-2 Analysis” but also in longer “N-grams” analysis samples.
Below, you will see some of the POS Tags.
- CC coordinating conjunction.
- CD cardinal digit.
- DT determiner.
- EX existential there (like: “there is” … think of it like “there exists”)
- FW foreign word.
- IN preposition/subordinating conjunction.
- JJ adjective ‘big’
- JJR adjective, comparative ‘bigger’
All of these Part of Speech Tags help Search Engines to understand the content within a context. Thus, knowing these tags help an SEO to understand a sentence from the perspective of a Search Engine in a deeper way.
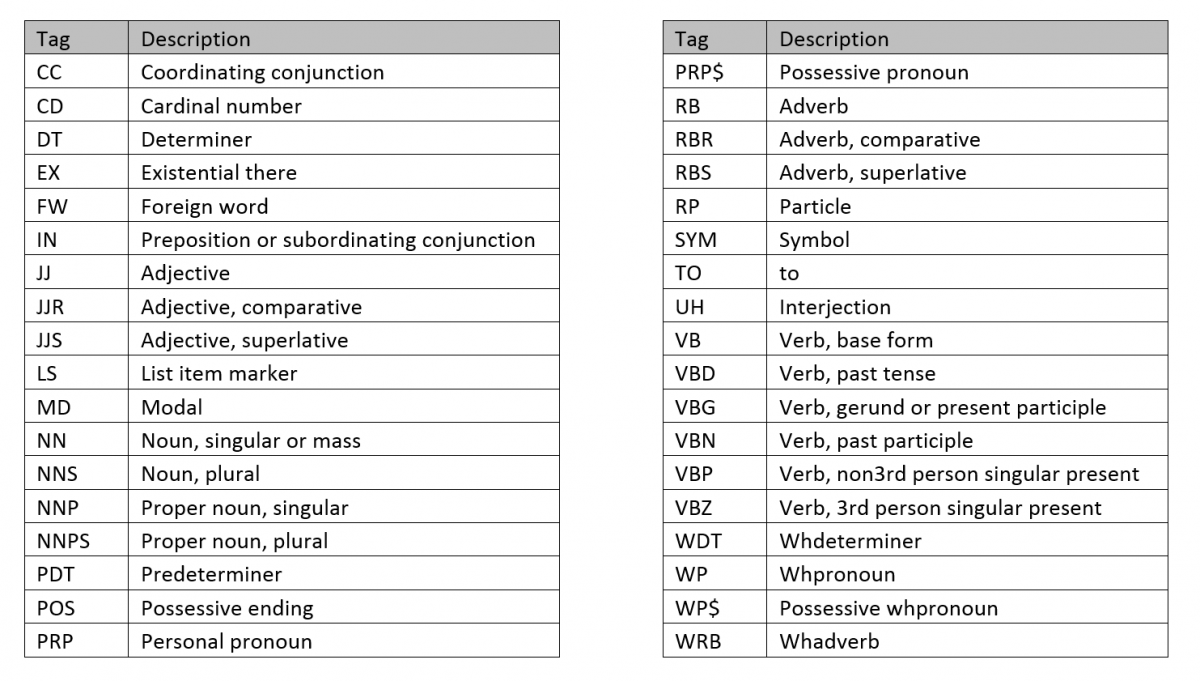
Why is Part of Speech Tag Important?
Content Format and POS Tag sections are related to each other. If there is a “comparison” search intent in a user query, the POS Tags below will come to the fore.
- JJR Adjective, comparative
- JJS Adjective, superlative
- Adverb, comparative
That’s why if you use “best, biggest” or “comparison” words in a query, Search Engine will try to choose these POS Tags from the content. If you use “best 5” in a query, Search Engine will try to find a “list” or list-like content format with matching POS Tags.
In short, I always educate my authors to think in a perspective of Search Engine so that they can include every bit of information with a better understandable content format and sentence structure along with right word combinations.
“You shall know a word by the company it keeps”
What is the Sentiment of Content Sections for Certain User Needs?
The sentiment of a sentence is actually not a ranking signal. And, Bill Slawski has a long and long article about this that includes valid reasons. But, still, the sentiment of a sentence can affect the users’ perception toward a topic. I believe that you see a “negative”, “threatening”, “stressful” sentence on the web every day, and also I believe that this doesn’t help a user who seeks information, methodology, and solution.
Barry Schwartz performed a review with Sarah Teach from Motley Fools and she used a term called “Heartfelt SEO” in the review.
Note: I have used “two different” entities with the type of person in the sentence above. And, then I have used a pronoun as “she”. If both of the entities’ gender would be “female”, then the pronoun “she” wouldn’t help too much since it creates uncertainty. In the Natural Language Process, this is called a “coreference error”. In short, the author is referencing someone with a pronoun, but it is not clear.
Such a situation would tell Google that the article may not be well structured, or written carefully. Also, Google wouldn’t record the “Heartful SEO” term with a relevance for Sarah Teach since it includes uncertainty. Thus, an article always should have a “clear” structure and every entity should be specified clearly with their context.
In this example, Barry Schwartz is an entity, and of course, I am talking about Barry Schwartz (Search Engine Optimizer, according to Google Knowledge Base), not Barry Schwartz (American psychologist). And this is also called “disambiguation of the entity”.
When I use even these two entity names in the same sentence, Google may check other co-occurrences of these entities on the web and clearly find the “interview” that I am talking about, or Google might expect me to put it right there for further disambiguation and relevance? That’s why you will find the related interview at the end of this note.
Heartful SEO and sentences with empathy are more useful for users in terms of adaptation of content by the user and it makes esay to digest the content.
Why is the Sentiment Structure of a Content important?
Heartful SEO and sentences with empathy are more useful for users in terms of the adaptation of content by the user. But also, I always tell my authors that you shouldn’t use “negative sentences”, “hateful words”, “complex analogies”, “stressful and bad possible outcomes” in the content. Also, since our industry in this SEO Project is actually “language education”, showing that we understand the users and showing them the solutions with deep empathy, help us for improving Real-World Signals toward our website.
And, as an SEO, sometimes I try to find mutual points and patterns for the best-ranking web page’s sentiment structure to create a better sentiment structure on my own content network. Sometimes, also I request help from authors.
What is Named Entity Recognition?
Named Entity Recognition is the recognition of entities in a content during Natural Language Processing. With the recognition of Entities, Search Engine can understand what the content is about, the context of the content, and what level of information it contains. Each Entity is linked to another in a semantic and hierarchical structure with a specific attribute.
Thus, the linking of entities in a content with the correct information and attributes they contain means that the relevant author is an expert on the subject for Google and that the relevant content contains more information (Unique Information Gain Score) than other similar content.

Why Is Named Entity Recognition Important?
In the educational process of writers, I always use the following slogan.
“Focus on Entities, not keywords.”
Therefore, while satisfying a certain search intent group in a certain subject within a certain context, all relevant entities must be associated with the detailed information, attributes and facts they contain within a context. At the same time, covering all relevant entities with the most accurate information by providing a wide Topical Coverage in a Topical Graph will provide Topical Authority for the relevant Brand-entity.
For Sources with Topical Authority, Google uses the term “Seed Sites” or sites with a high “SourceRank” in their patents. These sites are authoritative enough to be a source for the Semantic Search structure created by Google itself, for example Wikipedia.
What is the Entity Type Matching?
Entity type matching is the matching process of types of terms in the query and in the candidate answer passage. If the entity types are matching, there is a strong probability that the candidate answer passage is an answer for the processed query.
At this point, many different concepts that we handle such as Content Format, Part of Speech Tag, Entity Connections and Attributes, Dependency Tree, Question Generation from Content come into play.
Entity Type and Entity Attributes in a query will be matched with content with the correct content format by including the relevant Entities in the specified Context and the specified Heading Vector, with the most understandable Dependency Tree.
Why is Entity Type Matching Important?
Entity Type Matching is important within the scope of the Featured Snippet Algorithm. “What is the best temperature for X?” In answering the question, the author should pass a concept related to temperature such as “Celsius or Fahrenheit” in the “Candidate Answer Passage”. Visuals are also important for Entity Type Matching. In Visual Ranking Algorithms, “Object Entity” and “Attribution Entity” detection systems help contextual discovery by recognizing objects placed in the relative. Search Engine now increases the context signal of the content for the search intent by placing images in both Featured Snippets and normal Search Snippets.
Therefore, I taught my team that they should always use the concepts that match the concepts in the question in the cleanest and most visible-understandable way. We have supported this with the objects in the visuals and the superstitions.
What is the Content Section for Initial Contact of Users?
Initial Contact refers to the first time the user communicates with the content. Content Section for the Initial Contact should include the most important terms that reflect the visit intent of the user. To create the best possible and comprehensive Initial Contact with the user, Dominant Search Intent, Sub-search intent should be analyzed. According to Google, the Search Intent Order and the Content-Type Order should match the users’ needs with the best possible order.
Thus, consolidated long-form content with multiple search intent can be created, this means that you will create fewer pages to satisfy users more. Also, this will make the crawling and indexing process easier while letting you create more authoritative content.
Canonical Query, Canonical Search Intent and Ranking Signal Dilution in terms of Initial Contact Phase with Users
I also have published another case study for a YMYL and Biggest Sexual Health Brand from Turkey. It is mainly focused on Technical SEO with “Ranking Signal Dilution and Consolidation“. Simply, summing up these terms can create more clarity about this chained SEO Terminology within a specific context.

Ranking Signal Dilution is the error of that two web pages compete for each other for the same canonical query and canonical search intent with very similar content or mutual content points. Thus, creating “distinctive” web pages with “distinctive” content for completely different search intents with a certain contextual hierarchy is also helpful for preventing ranking signal dilution.
That’s why internal links, Topical Connections, and Borders are also important terms.
Dominant Search Intent is also the “Canonical Search Intent”, which means that lots of different queries have the search intent mainly.
Canonical Query is another term that includes “Query Rewriting”. Query Rewriting is the process of rewriting the users’ queries to serve better Search Results. Users can use different queries for the same search intent, the best summative version of a query is actually the “Canonical Query”. And, in the initial contact section of the content, the canonical query and their “variations” should be included for a better “Neural Matching”.
Topical Hierarchy, Contextual Hierarchy, Topical Coverage, Canonical Intent, and Heading Vectors are the related terms with the Initial Contact Section of the Content. If this section talks about something different than the users’ main search intent, the web page will be weaker according to its competitors in terms of user-satisfaction possibility score and also relevance.
Why is the Content Section for the Initial Contact with Users important?
If the initial Contact Section of the web page is not optimized in terms of length, terms to be included, tone of language, and visual communication, it might be outranked by its competitors. This might also affect the rest of the web page’s performance.
In every webpage, the best-ranked terms and best successful keywords can be found in the first section of the web page since this section reflects the web page’s actual purpose.
Initial Contact Section of the Content and Passage Indexing/Ranking Relation
Since most people don’t know SEO or Advanced SEO, most of them create unnecessarily long-form content without any categorization, optimization, organization, and structuring of the content. Thus, the search intent may not be perceived as distinctive and can be diluted in the content.
Also, long-form content can make the bottom section of the web page more diluted in terms of Ranking signals since its position is at a deep level of the web page and irrelevant to the main theme of the web page.
Google decided to start its “Passage Ranking and Indexing” algorithm in this context. If you don’t know how to organize a Topical Graph and Cluster within your website for Semantic SEO, Google might give a passage ranking boost for the most relevant queries and ignore the rest of the web pages so that the content sections may not dilute each other in terms of dominant search intent.
A web page can be good enough for a query while not enough for another similar query. With Passage Ranking and Indexing Algorithm, a web page still can rank high for the queries that the content is good enough while for other queries it may not get the best ranking. Thus, every content section can be evaluated within itself.
But, still, Passage Ranking and Indexing will only affect the 7% of the queries and most of them will be really long-tail queries, and I believe Reddit, Quora or other kinds of Question / Answer sites will benefit from this more than brands and content publishers.
With Passage Ranking or without it, you still need these terms and the semanticization process of your website, along with Natural Language Understanding capabilities.
What is Search Engine Communication?
Search Engine Communication is the process of understanding the Search Engine’s perspective, its signals, behaviors, and reflexes while communicating with its algorithms via small and big changes on the web. By understanding the Search Engine, managing an SEO Project can be easier and more result-oriented.
A Search Engine can’t always tell its algorithms or what it wants to see to the SEOs since it will eventually let SEOs exploit algorithms of Search Engines. Because of the “Trust Issues” between SEOs and Search Engines, nothing can be told with pure “clarity”. But still, if you have strong analytical skills along with a strong memory, you can communicate with Search Engine’s algorithms.
Since Search Engines work through Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence systems, you simply can give consistent, continuous, semantic optimization signals to the Search Engine so that its algorithms can trust you as a reliable Source on a given topic.

Why is Search Engine Communication Important?
During the SEO Case Project, by publishing articles with regularly increasing frequencies, publishing articles within sub-topics with a logical order, adding semantic consistency and logical connections to the content clusters, using semantic Content Formats for every semantic question type, I have made the web-site pretty easy to understand for Search Engine and use it as a reliable source for its own niche.
Thus, with semantic structures and behaviors, you can train the Search Engine’s AI Systems and communicate with it.
Hreflang is the attribute for specifying the different versions of a web page in terms of regional, language, or country-based differences. And, it helps for crawling the website, but it also helps Search Engines to categorize the website for different search intents based on geography and language differences. This is the official statement of Search Engines.
Hreflang attribute shares the PageRank of a web page with its alternate versions, also it shares the probability of satisfaction of users with a certain amount of queries. Along with historical data of the web page, it also shares the authority of the web page and web page segments’ prominence with alternate versions.
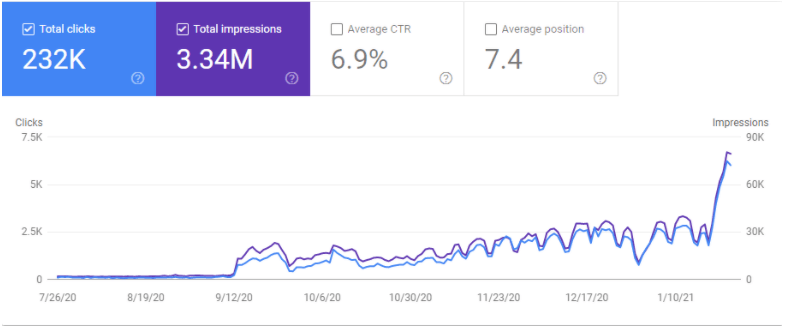
Below, you will see the same effect for 28th day of January.
This is the non-official statement for Search Engines.
Before, 1 August 2018, the Medic Update, this was a blackhat technique that I was using. In the old days, you could send a sitemap for any website with the “pinging” method. And also, you could send a sitemap with the “hreflang” attributes.
So, imagine that you are sending Google a sitemap for Wikipedia.com and marking your own URLs as their “alternate versions”. This was creating a huge ranking boost in the Black Hat SEO. Since this method doesn’t work anymore, I can say this easily. But this helped me to see how Google shares PageRank between alternate versions of a web page. Isn’t this also a Semanticization of the website? If the canonical version is quality, the alternate version should be quality too right? This, how Machine Learning works… But also, if your alternate versions are not quality, it also can affect the performance of, canonical version.
So, since my articles with alternate versions were semantically great and algorithmically authored with content engineering, I have had another boost in terms of ranking. And, since I create more great content for Google’s users in other languages too, it helped me to outrank my competitors. Since my competitors try to satisfy Google’s users without a semantic organization and help the quality of Google’s index only for a single language, I have more advantages.
If you want to learn more about canonicalization, I recommend you to read our Canonical Guideline for SEO.
What is the Query/SERP Mapping?
Query SERP Mapping can work in a “language-agnostic” way. Google always tries to create the same type of SERP for different languages and regions as long as the entity type and search intent are the same. Thus, Google can unify more data from the user to understand its behaviors, more data can be used for greater algorithms and more efficient A/B Testing.
In other words, Entities are language-agnostic and an entity-based Search Engine or Semantic (Structured) Search Engine is also language-agnostic. You can come across Query/SERP Mapping with also the name of “Keyword Mapping”. This basically is the process of understanding the SERP and Topical Borders between different Neural Nets so that you can understand whether you should open a new page or not, or how you can create the best Semantic URL and Internal Link Structure?
Also, do you need video marketing? Are the images important? Local sensitivity high for these queries or not? Query/SERP Mapping can give this to you.
And, if there is not a Featured Snippet for a query, you simply can check the same “search intent” with different languages. If in other languages there is a featured snippet, you also can trigger a Featured Snippet for the same search intent for your language-based SERP.
Lastly, you also can check the People Also Ask Questions, Knowledge Panels, News, Images, Videos verticals of search, you can change the “date” filters with the “tools” section to seek mutual patterns between SERP Snippets to understand what is required for this query?
And, you can check which sentiment structure, content length, unique information, and which content format can be the best option for that query group.
Why is Query/SERP Mapping important?
You may see the importance of Query/SERP Mapping, below.
- I have created a “less” page than my competitors.
- I have satisfied more users’ intent with fewer pages.
- Thus, I have created more consolidated, easily crawlable, and understandable web pages.
- All of my content networks are Semantically Adjusted according to Google’s SERP Design for the same search intent group. If there is a list in the Featured Snippet, I have used lists. If there is a better Featured Snippet format possibility, also I have used it.
- I have understood which content should be linked with which words from where to which content from only Google’s SERP.
- I also adjusted Heading Vectors, found Questions to be generated, and organized the contextual capacity, and analyzed the unique information gain score opportunities via only Google’s SERP.
Note: I also recommend you to take a look at the Search Engine’s second and third pages, you will see a strong difference between pages on the first page and the pages on the third page. Also, you should check Bing’s SERP too, it can help you to improve Google’s index too, and can supply your content briefs with more unique opportunities.

Topical coverage is a metric about the level and competence of a website on a topic. If a source does not have enough content about a topic, its topical coverage will be low. At this point, the way topical borders and topics are linked together is critical to Semantic SEO.
At this point, the Topical Connections concept comes into play. The context in which you cover the topic is as important as your covering a topic. For example, if you examine a page speed topic with developer concepts, Search Engine will handle related content in this context, if you examine it with SEO concepts, it will handle it in the context of SEO.
About, Topical Coverage, Authority and Expertise, you can find a relevant quote from John Mueller below.
Yes, that’s always useful. For search engines, you are building out your reputation of knowledge on that topic. For users, it provides more context about why they should trust you. Also for search engines, if Google can recognize that a site is good for the broader topic, then it can surface that site for broader queries on the topic as well. Google doesn’t have to focus on individual pages to surface the site for that broader topic.
John Mueller, Google Webmaster Trends Analyst
The quote is from 5th February of 2021, you can also watch the John Mueller while saying these, from the video below.
Topical Connections is about how the contents of a website are in which subject and how they are connected to which subject. The main point here is that you think of the Content Network as a slowly weaving network. This makes it possible for you to obtain a Topical Authority over time in the context you choose.
Why are Topical Connections Important?
Since this website is about “English Learning”, I only focused on “educational context” and connected every content to each other with this perspective. But at the same time, I have placed the topics to be covered in a queue.
I haven’t yet covered the most searched topics and most important topics in any way, on this site where I generated organic traffic growth from 0 to 100,000 in 115 days. If I had covered these issues first, they wouldn’t have any visibility because there was not even a topical authority, topical coverage for my website.
However, now that I get coverage and authority in many subtopics in the same context when I cover the most important issues, we will see that this traffic increases much faster.
Topical Connections is a guiding metric for me on how to positively influence Topical Coverage and Authority metrics by linking what content to which content in what context and when publishing which content.
What is the Semantic SEO’s Effect for Crawl Efficiency?
Also, if you publish your articles with a semantic order, logic, and hierarchy, the Search Engine will understand that you follow its Entity-based Search Results Page’s order. With contextual internal links, you also can strengthen this signal, and Search Engine can know that when it crawls your website, it will find useful, quality and understandable, clear content for a given topic and group of related search intent groups.
Google uses Machine Learning for organizing the crawling resources so that it can organize the crawling cost while finding the best useful content per crawling cost. So, even if you don’t use Technical SEO, thanks to Semantic SEO and Search Engine Communication, Google still would be able to crawl your website with efficiency and understand your content faster. If Google understands your content faster so that it can know what to rank it for which search intent groups and query groups, it also will help your Crawl Efficiency and Quota.
After crawling the web site, even after the indexing, Google continues to spend its resources to rank your web site for the best-fitting query group, so an understandable, clear, and semantic content network also helps for “Evaluation Cost” of your web pages.
If with time, your content can be successful with its visitors, it will also give the signal to the Search Engine that it made the right decision. And this loop will create a Search Engine Trust for your web site.
Of course, in this SEO Project, I have experienced the negative effects of lackness of Technical SEO, as I have told, but with Semantic SEO, I have at least decreased this effect.
Note: Evaluation Cost, Search Engine Communication, and Search Engine Trust are three different terms that I use, if you have a better suggestion for these meanings, I also can use them.
What is Page Segmentation for Search Engines?
A Search Engine wants to try to understand the web page segments according to their functions and content. “Boilerplate Content ” amount will affect the “similarity” level between web pages. If the Boilerplate Content is excessive according to the main content, this will affect the main content section’s prominence in a negative way. A web page’s main focus should be on its main content instead of the header, footer, sidebar, ads, or pop-ups.
To understand which links are more important or which content sections are more important for that specific webpage, Search Engine segmentify the web page so that it can weight terms, links, text, image, and other kinds of content according to their prominence.
That’s why using a consistent header and footer like said in Google Quality Rater Guidelines helps users to understand the web page faster while helping Search Engine to determine what the main content is for these web pages.
Search Engine’s Page Segmentation methodologies can vary. They can look at “logos, function blocks, visual design elements, HTML Structure” and more to segmentify the webpages.
Why is Web Page Segmentation Important?
Since I don’t have nearly 0 content on my boilerplate content, all of the web pages only occur from “main content”. 70% of links and 95% of content are actually in the main content.
Also, since I don’t have a long and big boiler-plate content, the web pages were light even if I don’t use any kind of page speed optimization for these webpages, still, they were light in terms of size.
Page Similarity or Content Similarity between web pages were less than 6%. This makes them unique and oriented-focused on only the users’ search intents.
This was an experiment on my side. I have thought like a data scientist and I wondered would Search Engine give more weight to the terms on the main content along with PageRank to the links on the main content. And, I didn’t see a negative effect from lackness of header and footer. I have put only the content that is relative to the web pages, mostly.
What is the Initial Ranking of a Web Page?
Initial Ranking is the first phase of a webpage’s ranking situation after it is getting indexed. If a web page is being shared on social media, if it doesn’t have any canonicalization or cannibalization issue, if it is in the sitemap from the first day while it is being linked site-wide, it can show better performance and can gain authority and better historical data on the SERP by time.
A Search Engine can have tens of different “reranking” algorithms for a web page according to the other kinds of differences on a website, webpage, or group of websites. So, the “Reranking” process of a webpage can be affected by the web page’s initial ranking situation.
You might see some differences in organic search performance between web pages that are in sitemap and not during the indexing process. And, this effect can be seen after months too. So, giving a priority to the newly published articles, products or webpages is a necessary situation.
Why is Initial Ranking Important?
In this SEO Project, I always tried to publish the articles in social media accounts, linked them from the sidebar, and we have put all the necessary internal links and anchor texts after the content is being published.
Let’s give an example with the “Topical Graph” in the context of “Initial Ranking”.
If you have a “Topical Authority” and “Topical Coverage” within a “Topical Hierarchy”, you also will get an Initial Ranking advantage on your side. So, your first articles within a topic, may not be in the best situation in terms of Initial Ranking, but if you clearly construct a hierarchic Content Network and logically order your content publishing schedule for different sub-topics and search intent, you will see that your website will get better ranking on SERP easier and faster.
So, that’s why I still didn’t write the most traffic-producing, most searched topics and articles for this site, there is a perfect time for writing them and closing the Topical Gap between my competitors.
What is the Impact of Neighbor Content and Website Segmentation?
Website segmentation is the segmentation process of the website’s different page groups in terms of their functions, services, content along with their URLs and On-Page elements. Different Website Segments can have different “crawl demands”, “crawl rates”, “site quality score”, “authority” and user-satisfaction possibilities in the eyes of Search Engines.
Neighbor Content is the content sections that are in the same Website Segment. Since all of the Neighbor Contents are basically in the same Topical Graph within the same topical hierarchy, a bad, thin, and unqualified content within the same “Content Cluster” can risk other contents and also affect the Topical Authority and Expertise of the rest of the Website Segment.
Why is Neighboor Content and Website Segmentation Important?
If Google can find an efficient web-site segmentation that complies with its SERP/Query and Search Intent Map, it can understand your website faster.
If every website segment has a quality content cluster, it means that Googlebot will crawl these pages more, and also it can increase your crawl quota, since whenever it crawls your website segments, Googlebot finds more useful, unique, consolidated, relevant, and informative content.
If the content is bad or also “slow”, it can affect other content’s performance in terms of Organic Search Performance.
What is the Featured Snippet Oriented Content Marketing?
Featured Snippet Oriented Content Network is the process of creating a content network that solely focuses on the semantics of featured snippets, “People Also Ask Questions”, “Knowledge Panels”, and Dynamic Organization of SERP. Featured Snippet Oriented Content Marketing focuses on creating a content marketing strategy that fits in every answer, information, and function it includes into Google’s SERPs’ nature.
From language structure to internal links or all of the Natural Language Processing terms, every bit of this SEO Case Study was for taking all the featured snippets, PPA Questions, Knowledge Panels, and more as much as I can.

So, that’s why I have lost half of the traffic on the 14th and 15th November during a Google Minor Update.
Why is Featured Snippet Oriented Content Marketing Important?
Google uses a different algorithm for choosing its featured snippets. There are lots of other patents for this process with the term “Candidate Answer Passage” scoring, adjusting, choosing, ranking, etc… And, these are the topics for another day.
But there are three important things here.
- Featured Snippets work within a semantic structure.
- Featured Snippets show the Search Engine’s trust for a Source for that topic. (Sometimes, a website can’t take a featured snippet since Google doesn’t choose it against its competitors.)
- Featured Snippets are not directly related to the “backlinks” or “historical data” of the Source.
- Featured Snippets can create historical data and authority for my domain within the given topic in the eyes of Search Engine and Users.
- If you have a featured snippet for question B, and if you satisfy the user, thanks to your semantic structure the Semantic Search Engine’s algorithms will also try your Source, for another related semantic question, such as A.
Thanks to hierarchical and logical structured web pages, every Featured Snippet can trigger another one for the website that is optimized with Semantic SEO.
Since I have a well-structured and clear answer for every question that can be generated from all of this content, everything that I do for this SEO Case Study is actually based-on featured snippets.
So, I also know that a featured snippet has less than 340 characters and 40 words, usually. So, in my content Briefs, I use the “FS” word to show that my authors that this “heading” and its answer is for the featured snippet. Then, they follow Google’s SERP and sometimes I put the screenshot of the featured snippet so that the author can see the “clear structure of the existing FS with the terms and NLP Rules as I thought them”.
And, Featured Snippets were my only chance to get this kind of traffic with this kind of period.
Since they are not related to the “Domain Authority”, I can simply outrank any kind-of authoritative domain for that given topic, in the shortest possible time.
So, that’s why when I lost most of my Featured Snippets after my server crash due to an excessive amount of traffic and Google’s minor updates on 14th and 15th November, I have lost half of the organic traffic.
And, that’s why I am actually, writing this case study because overcoming 1 Million / Month of Organic Traffic in 8-12 months will be way much harder.
An Executive Summary for Semantic SEO Case Study in the Light of SEO Theories
The concepts we have learned so far are listed below, absorbing all these concepts and understanding the relationship between them can allow you to challenge websites with the greatest authority, even with a brand-new domain.
- Topical Coverage
- Topical Graph
- Topical Authority
- Topical Connections
- Topical Hierarchy
- Topical Borders
- Semantic SEO
- Semantic Search
- Contextual Hierarchy – Conceptual Hierarchy
- Entity Type Matching
- Neural Matching
- Neural Nets – Sub-topics
- Dominant Search Intent
- Sub-Search Intent
- Contact Section of Initial Contact
- Content Format
- Update Score
- Update Amount
- Update Frequency
- Content Publishing Frequency
- Link Types (S-Nodes, I-Nodes, C-Nodes)
- Heading Vectors
- Context Vectors
- Candidate Passage Answer
- Dependency Tree
- Part of Speech Tag
- Sentiment Structure
- Named Entity Recognition
- Entity Association (Connections)
- Entity Attributes
- Complex Adaptive System
- Knowledge Domain
- Query/SERP Mapping
- Crawl Efficiency
- Search Engine Trust
- Search Engine Communication
- PageRank Sharing of Hreflang
- Semantic (Structured) Search Engine
- Question Generation from Content
- Unique Information Gain Score
- Initial Ranking
- Page Segmentation
- Topic Cluster – Neighbor Contents
- Website Segmentation
- Featured Snippet Oriented Content Network
- Content Similarity Level – Boilerplate Content
- Ranking Signal Dilution and Consolidation
- Canonical Query
- Canonical Search Intent
And, now you can read the practice of this process, you might understand better what I did with which reason. Also, if you wonder what “Ranking Signal Dilution, Canonical Search Intent,
I know some of you will think that the Executive Summary is the best and useful section of this Case Study, but it is definitely not. The theory is the mother of Practice.
I have tried to decrease the link count on the web pages as much as I can while increasing the relevant link amount in the main content as much as I can.
This was an experiment for me and it worked well. I didn’t need a header-footer link structure but also, I will use a “contextual navigation” on this site, in the future while the SEO Case Continues.
Importance of Link Count and Contextual Relevance within Links
The lesser the link count on the page, the more PageRank will be shared per link according to their features, positions, styles, etc… By putting at most 3 internal links with relevant anchor text into the main content, I have shared the best possible PageRank, Relevance, and Context between my internal web pages.
What is the Effect of Lackness of Technical SEO?
You might think that like Matt Cutts said in 2008 the first time the key of SEO is “great content”. But I think the key is still “Technical SEO”. In this SEO Case Study, I have performed an experiment with the SEO Terms that I learn from Search Engines’ Patents. I have tried to see their perspective’s practice effect on the SERP and I succeed in it.
But, this doesn’t mean that I couldn’t do better. I still have 250 web pages waiting to be indexed. And, also I have more than 50 pages orphaned.
This means that, with Technical SEO, probably I could get more traffic like 150.000-200.000 Organic Visits / Month in 115 days.
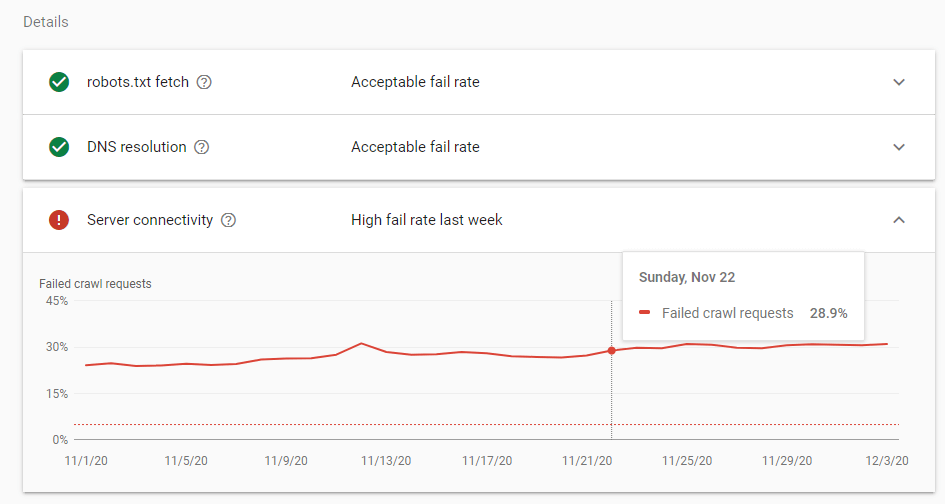
Besides the design, layout, page speed, brand power, site navigation, also the “server’s” situation was pretty bad. I am emphasizing this situation to show to real difference maker for this Semantic SEO Case Study.
What was the Effect of Hreflang?
This section is related to the “Hreflang’s PageRank and Authority Sharing effect”.
After I have implemented Hreflang, in 2 and half-day, I have seen a traffic increase of more than 100% in other countries. And my organic query gap with my competitors is more closed with the targeted sub-topics.
With What Frequency Do I Update Content Blocks?
You should remember the concepts of Update Frequency, Update Amount, Update Score while reading this section. If you change only the Title Tag, Meta Description data of a web page but not the content, it will only show to the Search Engine that you have made a change for SEO. In this SEO Project, I did not use or optimize the SEO Tags, which are one of the “On-Page SEO” elements, in any way, I left everything to Google.
Title Tag is actually the root of the content. If you change it, the Search Engine might change the context of the content of that page while reranking it.
But, after publishing any article, I have updated them for adding the anchor texts that are relevant for the newly published content. All of the anchor texts were actually ready to be linked, they were just waiting for the next related article so that they can be linked together.
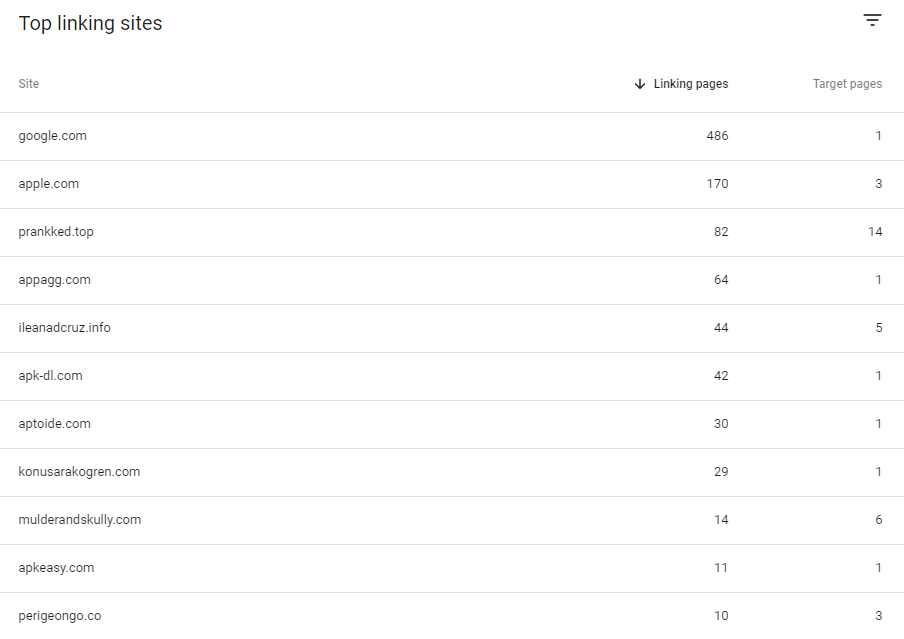
These are the Top Linking sites of the Getwordly, as you can see, they don’t have value in terms of Branding or Contextual Authority.
And, I always check what the author writes and what I write into the brief so that I can audit the content’s complement level with my briefs. If they are not well-structured enough, I make authors revise them.
So, I didn’t update any content for just “updating” it and faking the “Freshness of Content”. Google knows what change you did what for while comparing the old and new content on the same URL. And, I didn’t have a time pattern for updating any content since I want Googlebot’s AI System to think that I can update my content every second so that it can keep my crawl frequency high. If you make regular changes at regular times, Googlebot will come and go only within this regularity.
Why did I lose all of the Featured Snippets during the 14-15 November Google Update?
During the SEO Project, I only focused on Featured Snippet Oriented Content Marketing with the scope of Semantic SEO. I didn’t use Technical SEO or any other kind of SEO Rules here. So, I can’t blame my customer because he didn’t buy the best server before, because warning the customer is actually my responsibility.
I could have understood that the server would crash soon from the crawl rate and frequency of Search Engine Crawlers along with the Log Analysis, or simply I could check the server’s situation.
Since I have started to take 7500 clicks per day, the server didn’t have enough power to supply the website. On the same day, Google has started a new Google Algorithm Update, they have decreased the Featured Snippet amount by 2.5%. And, since my website was not responding, I have lost most of the featured snippets in just one day.
I have told my customer that it will be fixed in 20-25 days because I have experienced another big server crush for one of my other SEO Case Studies. In this example, it has recovered after 25 days, you can read my Hangikredi SEO Case Study that I have published with OnCrawl, it is also a Holistic SEO Case Study that focuses on the effects of Core Algorithm Updates.
And, as I said, it has started recovering.
What is the Current Situation of the SEO Project?
In the Current Situation of the SEO Project, I continue to create a more comprehensive and semantic structure for broader topics while increasing my topical authority for the current ones. Also, I have noticed that my articles are being linked in a prospecting way since they have more answers in the best way according to competitors’ ordinary content and random site-structure.
And, also I have three more websites with the same methodology I have created and improved the Organic Visibility from 0 to 100.000 + per month. I didn’t include them in this SEO Case Study Article because I know that only the people who really want to learn and interested in SEO will read this theoretical terminology, probably I will publish others with “shorter” articles for ordinary readers.
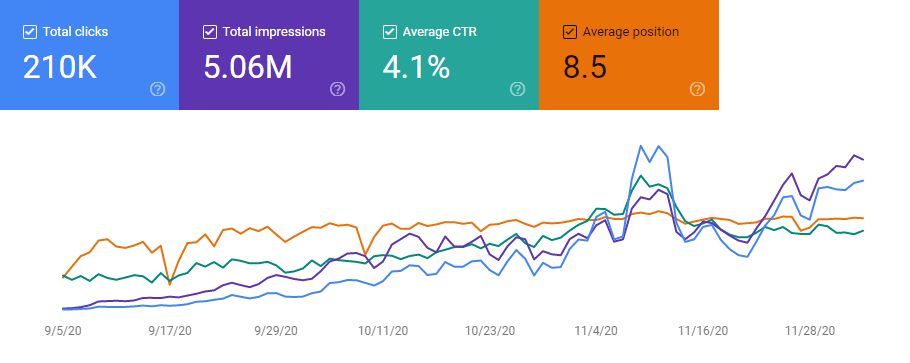
Last Thoughts on Semantic SEO within Holistic SEO Vision
This is the first and only SEO Case Study that I have published on Holisticseo.digital. I might continue to publish my new SEO Case Studies here. But, I will also unify this SEO Case Study with the coming articles for Site 2, Site 3, and Site 4, and I am planning to publish them on other blogs for more normal users and readers.

If you finish all of this Semantic SEO Case Study with all these SEO Terms and Theoretical Information along with Search Engine Patents, you know how I am obsessed with Search Engine’s nature and their algorithms. That’s why I am saying “normal readers”. About Semantic SEO and Holistic SEO, for me, Holistic SEO is a root term for the advanced SEO Concepts including different methodologies and knowledge from other disciplines such as Data Science, Data Manipulation and Front-end or generally coding. Thus, Semantic SEO is a part of Holistic SEO.
The purpose of this SEO Case Study is not that telling you that you don’t need Technical SEO or Pagespeed Improvements or Branding, Layout Improvements etc… Always approach an SEO Project, Holistically, the main purpose of this Case Study is that saying, SEO Terms and Theories, Google Patents and Analytical Thinking within Semantic SEO works well enough to prove its function, despite all the missing points of SEO and disadvantageous sides of these projects.
